Carbonation of concrete is a very important title to be aware of by civil engineers as it directly related to the durability of reinforced concrete.
Firstly, let’s see
What is the Carbonation of Concrete?
It is a process of reacting calcium hydroxide in the concrete with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and creates a calcium carbonate and water.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
This process starts with the concrete surface and it gradually moves towards the inner of the concrete. Carbonation of concrete is a slow and continuous process.
When the carbonation front reaches the reinforcement, it could start the corrosion of steel.
How does reinforcement Corrosion Occur?
The PH value of the concrete is lowered to about 9 during the carbonation reaction. The protective oxide layer around the reinforcement breaks at this level enabling the occurrence of corrosion of reinforcements.
The reinforcement is protected by the alkaline condition caused by the hydrated cement paste. This is neutralized by the carbonation allowing the corrosion in the presence of oxygen and moisture.
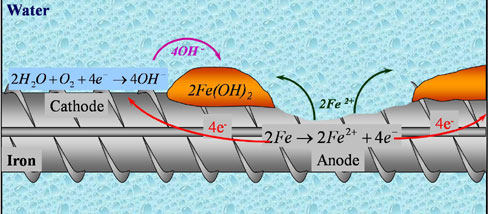
Continuing this process will increase the volume around the reinforcement and then cracks will appear in the cover zone by further exposing the reinforcement to the environment. In addition, spalling could also occur due to this corrosion with the increase in the internal volume.
This will affect the strength of the reinforcement leading to loss of its tensile strength.
The article on how to prevent corrosion could also be referred to information on corrosion preventive measures
Factors Affecting the Rate of Carbonation of Concrete
There are factors related to the concrete and external environment that affect the carbonation.
Let’s list out all those.
- Grade of Concrete
- Water Cement ratio
- Permeability of Concrete
- Cover to the reinforcements
- Ambient relative humidity
- Corbondoxide concentration in the area
- Surface protection
- Age of the Structure
- The orientation of the structure
- Admixtures
- Porosity of Concrete
- Curing period
The above factors are directly related to the carbonation of concrete and the changes made to those could reduce the rate of carbonation of rebar.
How to Test Carbonation
Depth of carbonation can be found very early with a simple test.
Phenolphthalein solution having 1% phenolphthalein is spray in the newly exposed concrete.
If the colour of the concrete change to pink, that area of the concrete is not carbonated. The area that did not change colour with the application of phenolphthalein is carbonated.
There are other methods such as IR spectrum analysis of carbonated concrete. The CO2 absorption by the specimen is measured in the method.
In addition, there are empirical methods developed to calculate the depth of the carbonation of concrete.

How to Calculate Carbonation Depth?
The following equation can be used to find the time required for carbonation up to the reinforcements.
t = (d/k) 2
Where, t – Time for carbonation, d – Concrete cover, k – Permeability of concrete
Using this equation, we can find the time required to carbonation front to reach the reinforcements. If we know the age of the building, we can check whether the reinforcements are affected by carbonation.
This can be used as an approximation method and the typical permeability of concrete related to the concrete grade could be used.
There are other similar nature equations developed with more parameters included to calculate the depth of carbonation.
Now let’s discuss the most important topic…
How to Avoid Carbonation of Concrete
The best way is to slow down the process as bringing down to stop completely is a very difficult task.
However, the following could be considered to implement to avoid/minimize the carbonation of concrete.
- Since the higher water-cement ratio contributes to the higher depth of carbonation, it could be controlled as possible.
- Adequate curing of concrete and extended curing period will help concrete to react well, and it reduces the cracking of concrete. Adequate curing reduces the permeability of concrete and as a result rate of carbonation will reduce.
- Use of admixtures to modify the pore structure and reduce the permeability of concrete.
- Additives like silica fume having a higher surface area could be used to reduce the porosity of concrete.
- The use of protective coatings will improve the durability of concrete and low down the carbonation process.
- It has been proven that self-compacting concrete has better performance against the carbonation of concrete.
Repairing of reinforcement corroded due to the carbonation of concrete could be done the same as the other repairs done when reinforcements are corroded.
Repair Concrete
- Clean the affected area properly and remove all loosen concrete.
- Clean the reinforcements.
- This could be done manually with a wire brush or a suitable chemical could be applied to remove the rust.
- If reinforcements are damaged in a way that it can not carry the tensile forces, that reinforcements should be replaced.
- Apply anticorrosive for reinforcements.
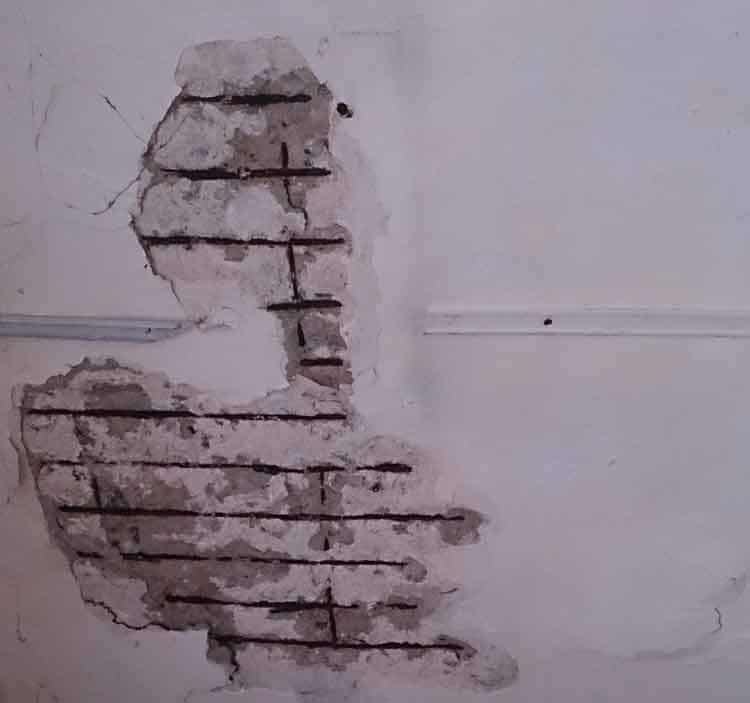

- Apply bonding agent for the concrete surface for better bonding.
- Apply a suitable mortar. This could be non-shrink concrete any applicable mortar mix approved by the structural engineer.


