As civil engineers are well aware, the use of concrete retarders has become increasingly important in recent years. They enable proper timing and usage of the various elements of a construction project, helping to ensure that the job is done properly and efficiently. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at concrete retarders and provide useful information for civil engineers considering their usage.
Any remaining workability is quickly lost once the primary stage of cement hydration begins, and the concrete stiffens to the point where it will form a “cold joint” if more concrete is applied on top of it. This will result in surface flaws and, in severe situations, structural weakness in shear due to a poor link between the freshly put concrete and the previous load discharged into the pour.
In hot weather and/or during large pours, where there may be a significant time delay in moving the placement of a concrete front, retarders are especially useful for helping with this issue. As the concrete gets closer to the initial set, they provide its principal benefit.
Concrete Retarders: What is a Retarder
Concrete retarders are substances that are added to concrete to slow down or delay the setting process. This can be useful in a number of different situations, such as when working in hot weather conditions or when there is a need for the concrete to set more slowly in order to avoid cracking. There are a number of different types of concrete retarders available on the market, and choosing the right one will depend on the specific needs of the project.
It is possible, though not always simple to delay, the concrete setting for practically as long as required by utilizing chemical retarders. The most popular retardants are made of sugar. The dosage of the retarder must be adjusted to account for the required amount of retardation time, the cement’s reactivity and fineness, the actual temperature of the concrete produced, and the surrounding temperature.
The retarder dosage should be adjusted for each unique situation by creating two to three trial batches, or in the most challenging situations, by employing a factorial design plan. It is also possible to slightly delay concrete setting or regulate the temperature of concrete in the summer by chilling it with ice and/or liquid nitrogen.
Effects of Retarders
Retardants work chemically on the cement to postpone the hydration reaction’s first stages. This should result in a longer period of workability retention as well as a delay in the mixture’s setting and hardening.
The only effective strategy to guarantee adequate workability at a delayed time after mixing is to start with a high initial slump, for example by using a greater plasticizer dose. In actuality, early workability loss is not primarily caused by cement hydration.
The following figure retarders behavior.
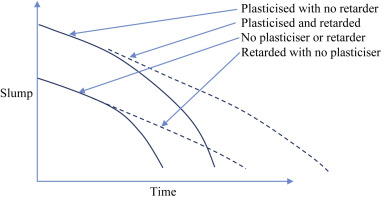
Strength
The use of concrete retarders would delay the early strength gain of the concrete. However, it would not affect the compressive strength of concrete.
Workability of Concrete
Regards would affect the workability of concrete. At the initial stage, it would increase the slump of the concrete. When we used the superplasticizer acting as water reducing admixture and retarder, could be subject to loss of the slump with time.
This would result in the segregation of the concrete with the low workability of concrete.
Slump Loss
As discussed, loss of the workability of concrete with time, the concrete slump will reduce. This is a common issue when we used modern admixtures.
Redosing is one kind of solution to address this issue. It could be done as recommended by the supplier and the maximum allowed dosage of the admixture shall not be exceeded.
Bleeding
Retarding the action of the concrete could lead to bleeding of the concrete.
Segregation
Segregation of the concrete connects with the stiffness of the concrete mix. Lowering the workability of concrete or the concrete slump could lead to this. Low workability of the concrete could be expected with it taking time.

Benefits of Using Concrete Retarders
One of the main benefits of using concrete retarders is that they can help to improve the working conditions for construction workers. In particular, they can help to avoid the dangerous and unhealthy situation of having to work in extremely hot weather conditions. By delaying the setting process of the concrete, workers are able to avoid the heat and stay comfortable and safe.
Another benefit of using concrete retarders is that they can improve the quality of the finished product. In some cases, it may be necessary to delay the setting of the concrete in order to allow for proper curing. This can help to avoid cracks and other flaws in the finished product.
Finally, concrete retarders can also help to improve the efficiency of the construction process. By delaying the setting of the concrete, workers are able to have more time to complete their tasks. This can lead to a faster and more efficient construction project.
Different Types of Concrete Retarders
As we mentioned earlier, there are a number of different types of concrete retarders available on the market. The most common type is calcium chloride, which is added to the concrete mixture in order to delay the setting process. Other common types of retarders include sodium gluconate, sodium bicarbonate, and ammonium sulfate.
Choosing the right type of concrete retarder will depend on the specific needs of the project. For example, calcium chloride is a good choice for hot weather conditions, while sodium gluconate is a better choice for projects that require a longer setting time.
Conclusion
Concrete retarders are an important tool for civil engineers and can provide a number of benefits for both workers and the finished product. There are a number of different types of retarders available, and choosing the right one will depend on the specific needs of the project.


