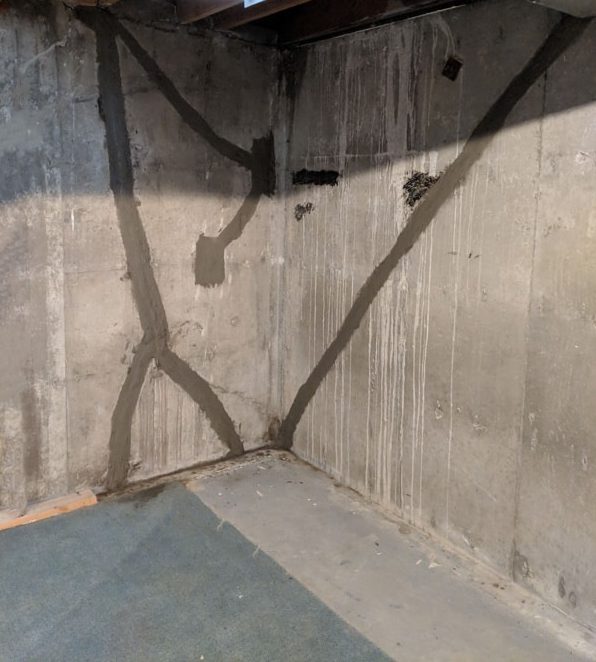
Cracks in basement wall could be due to the construction defect or failure in the design. The incorrect assumption made during the design could cause this issue.
In general, almost all types of construction elements get craked due to various reasons. The width of the crack will cause issues.
In water retaining structures, the crack width will be limited to 0.2mm to avoid movement of the water. Actually, water moves through the crack having a width of 0.2mm; however, self-healing will seal these cracks.
When the appearance of the surface finishes is important, we limit the crack width to 0.1mm in water retaining structures.
Sine we discuss the cracks in the basement wall, firstly, it is required to know whether the wall is in contact with water or not. In general, there are concrete walls, we could assume it is a basement wall retaining the earth.
In this article, firstly we consider concrete basement walls.

Cracks in Concrete Basement Wall
Cracking could be due to one of the following reasons.
- Design errors
- Thermal cracks
- Shrinkage cracks
- Restrain cracks
- Inadequate expansion joints
- Lack of movement joints where they required
Let’s discuss each type of crack in detail.
Cracks in Basement wall due to Desing Errors
Cracks in the walls could occur due to design errors. Lack of attention on the behavior of the wall or consideration of incorrect design parameters could cause this issue.
Some of the common issues are listed below.
- Lack of attention on lateral restraints
When the concrete wall connects with the foundation, there will be lateral restrain. If there is a free cantilever wall, the top of the wall is free to move. But at the connection of the wall and the foundation, there is no allowance to the movement.
This needs to be considered during the design and required reinforcement needs to be provided. One might miss providing adequate reinforcements.
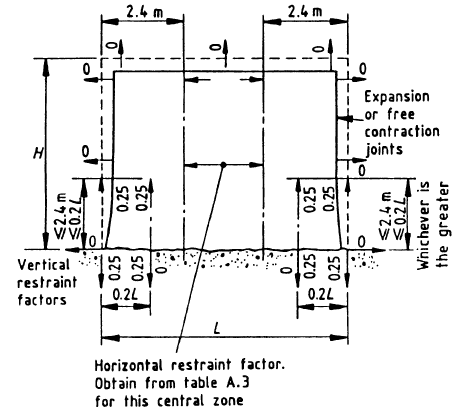
It is required to provide reinforcement in the horizontal direction to bear the lateral stress developed in the section considering restrain effect.
One might mistakenly avoid providing reinforcement in the horizontal direction for this effect.
The article Early Thermal Cracking [calculate R/F requirements] could be referred to for more information and calculation procedures.
- Temperature Rise During Hydration Process
During the hydration process, the temperature of the concrete core rises considerably. It is required to control the rise of the temperature.
The different measures could be taken discussed in the article Thermal Cracking of Concrete [a detailed study] could be done to avoid it.
In the absence of the mockup test, we do the calculation based on the assumed values. Incorrect or unrealistic values considered in the design will change the required reinforcement area.
Especially when the thicker concrete walls are constructed, the designer shall pay attention to the rise of the temperature in the concrete wall during the hydration process. If not, thermal cracks in basement wall and cracks due to the delayed ettringite formation could occur.
Thermal Cracks in Basement Wall
Concrete subjected to thermal cracks during the hardening process and during use.
Mainly, there are three types of thermal cracks as discussed in the article Thermal Cracking of Concrete [a detailed study].
- Freeze/ thaws cycles
- External seasonal temperature variation
- Early thermal contractions
Above mention, the article could be studied further information and measures to be taken avoid thermal cracks. Let’s see some occasion thermal cracks appears in the basement walls.
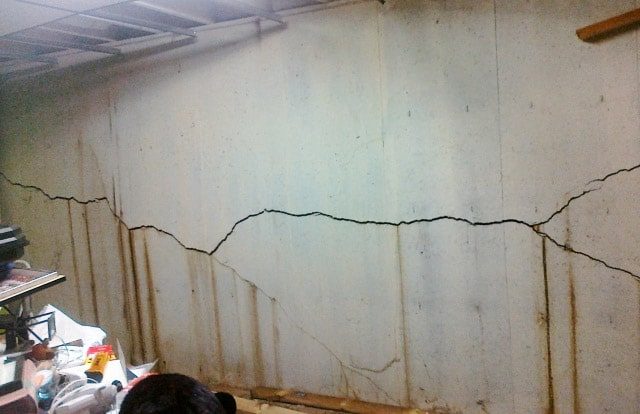

Attention shall be made to avoid the cracks by taking necessary action during the design and construction.
Shrinkage Cracks in Basement Wall
The volume of the concrete reduces with time and as a result, there are possibilities of cracking the concrete.
Namely, there are about six types of shrinkages observed in the concrete.
- Plastic Shrinkage
- Chemical Shrinkage
- Autogenous Shrinkage
- Drying Shrinkage
- Thermal Shrinkage
- Carbonation Shrinkage
The article Types of Shrinkage in Concrete [detailed study] discussed all types of shrinkage cracks.
Special attention shall be made to the curing to avoid shrinkage cracks.
Restrain Cracks
Under the design errors, we discussed more on the restrain cracks.
These types of cracks are solely due to the restraining effect of the wall.
Continuation of the wall needs to be considered in the design. If the wall is restrained in any direction, it shall be considered during the design. The following figure indicated some restrains considered avoiding cracks in basement wall.
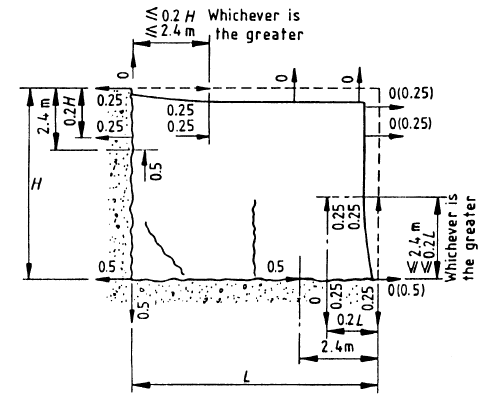
Cracks as shown in the above figure will appear in basement walls if they are not designed for the lateral restrains developed due to the other elements.
Inadequate Expansion Joints
Expansion joints in continuing reinforced concrete walls are required to allow lateral movement. The lateral movement of the wall could be due to the thermal action, shrinkage effect, etc.
If there are no adequate expansion joints in the wall, it could lead to cracking in the wall.
In a free cantilevered wall, there will be vertical cracks in the middle part of the wall. However, if we provide horizontal reinforcements adequately, cracking could be minimized.
In order to avoid cracking in the basement wall due to the lateral movement, we provide expansion joints. According to the ACI guidelines, providing expansion joints in the spacing of 6m-9m would be acceptable.
No movement Joints Where Required
In the location where the structural shape is changed, it is required to provide movement joints. For example, in the “L” shaped building, we need to separate two legs especially the foundation of the building will be a raft foundation.
You may refer to the article Types of Concrete Joints could be referred detailed information on this subject.
If there are no joints at corners, there is a possibility of cracking the wall.
Cracks in Brick Basement Walls
The basement wall could crack due to the thermal movement and settlement of the foundations.
Let’s discuss each type of crack in the basement walls
Settlement Cracks in Basement Wall
Part of the wall or area of the building could settle due to the weak ground condition or due to the failure of the foundation system.
These cracks propagate in inclination to the horizontal. We can judge these types of cracks with a visual inspection.
Especially, this type of crack occurs when there are concentrated loads in smaller building structures.
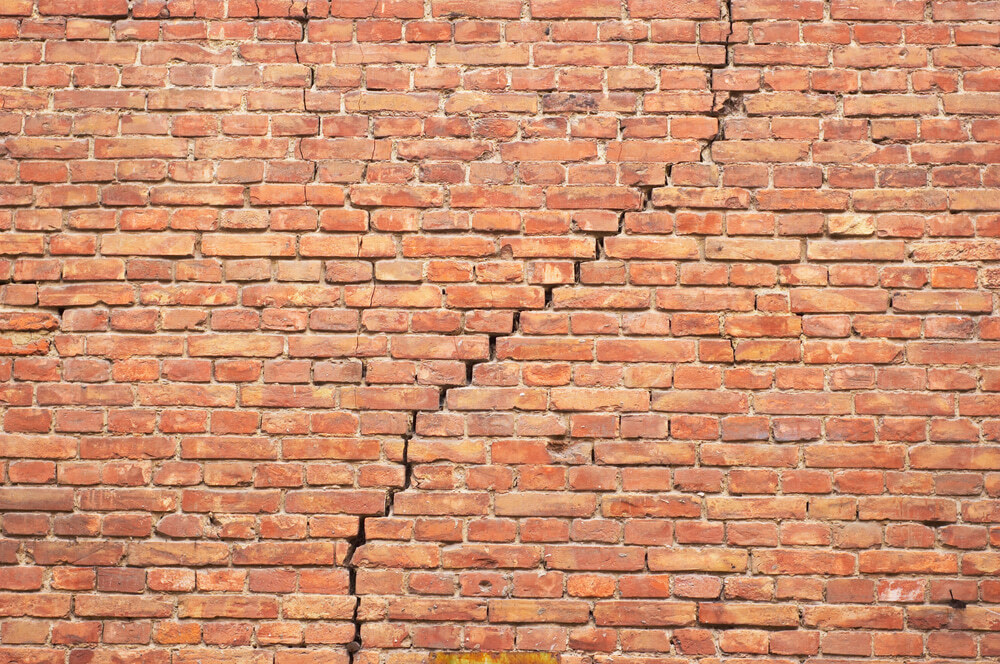

Brick Cracks due to Lateral Loads
When lateral loads are applied, there are possibilities in cracking the brick walls.
These cracks could be avoided by providing lateral restrains.