Strength of concrete or in other words, the compressive strength of the concrete, dominant factor considered in the structural design in addition to the strength of the reinforcements. The factors affecting the strength of concrete are must known to develop the required strength.
There are key factors as discussed in the article Compressive Strength of Concrete and Testing of Concrete that affect the strength of the concrete.
They are as follows.
- Quality of the materials such as cement, coarse aggregate, fine aggregate, and water
- Water Cement ratio
- Air entrainment
- Aggregate proposition (Coarse: Fine)
- The ratio of Aggregate to Cement
- Curing period
- Use of Admixtures
- Compaction of Concrete
- Time after concreting
Each factors affecting strength of concrete are discussed as follows.
1. Quality of Materials
Mainly there are four materials used to make the concrete.
- Cement
- Coarse aggregate
- fine aggregate
- and water
The effect of each of the materials can be discussed separately.

Cement
cement is the material that creates the bond between aggregate after reaction with the addition of the water. The hydration process can be represented by the following equation.

The use of quality cement improves the bond and strength. The strength of the cement depends on the date of the manufacture.

Similarly, there are several aspects that should be looking into when considering the quality of the cement.
- Date of packing
- Colour
- Rubbing
- Hand Insertion
- Float Test
- Smell Test
- Presence of lumps
- Shape Test
- Strength Test
In addition, there are other cement tests to be carried out to find the quality of the cement.
- Fineness
- Compressive strength
- Heat of hydration
- Initial and final setting times
- Soundness
- Normal Consistency
In general, cement is considered one of the highly influential factors affecting strength of concrete.
Aggregates
Aggregate is the material bond with the cement paste after reacting with water. Therefore, the quality of the aggregate effect on the strength of concrete.
Generally, 80% of the volume concrete is filled by aggregates.
There are two types of aggregates namely coarse aggregate and fine aggregate.
The following factors are considered to maintain the quality of the aggregates.
- Particle size distribution/gradation
- Shape and texture
- Moisture content
- Specific gravity
- Reactivity
- Soundness
- Bulk weight
The above mention characteristic influences workability, finishability, bleeding, and segregation of fresh concrete effects the strength, shrinkage, density, and durability of hardened concrete.
2. Water Cement Ratio
The water-cement ratio is one of the most important factors affecting strength of concrete. Depending on the water-cement ratio, the compressive strength is defined in the mix designs.
When we required a certain grade of concrete, firstly we select an appropriate water-cement ratio to proceed with the mix design.

As indicated in the above figure, the increase of the water/cement ration reduces the compressive strength of the concrete. Water/Cement ratio can be increased by increasing the water content or by reducing the cement content.
At present, the use of admixtures that reduce the content of water to be used to retain the expected workability has made a considerable impact on this ratio.
The use of new admixtures has brought more advantages to the industry and also the risk. All those will be discussed in the latter part of this article.
3. Air Entrainment
In general, air entrainment in the concrete reduces its strength.
An increase in the volume of air voids by 1% reduces the strength by 5%.
However, internally entrained air voids improve the resistance of concrete to damage from cycles of freezing and thawing.
Further, it improves the workability of the concrete.
The following figure also indicates the variation of the compressive strength of concrete with the water-cement ration based on the entrainment of air.

4. Aggregate Proportion
Aggregate proportions are greatly affecting the strength.
Usually, we have a fine and coarse aggregate. Sand and the quarry dust is used as fine aggregate.
All of these aggregates, their properties shall be checked according to the standards and the gradation of the materials shall also be within the acceptable range.
Whenever there is a change in the source of the material, verification shall be done.
Since the particle size greatly affects the compressive strenth, they shall be checked regularly.
In a concrete, mix proportions of cement, water, coarse and fine aggregates decides the strength of the concrete. Different strengths can be achieved for different mix proportions.
When the mix designs are done, mix proportion of the aggregates are considered as one of the most important factors.
5. Ratio of Aggregate to Cement
The majority of the volume of concrete is represented by the aggregates; fine aggregates and coarse aggregates.
Cement after reacting with water create the bond with the aggregates to create the concrete.
Cement content and aggregate volume ratio is related to the strength of the as shown in the following figure extracted from a technical paper.

6. Curing Period
The period of curing of concrete is directly affecting the strength development of the concrete. The article published in this website Factors affecting Curing Time of Concrete provides detailed information on the curing period of concrete.
The following figure extracted from the web site clearly indicates the effect of the curing period on strength development.

As indicated in the figure, and due to the importance of curing of concrete to gain its strength, curing shall not be avoided.
In addition to the strength gain, the curing of concrete improves its durability, cracking when it hardening, etc.
7. Use of Admixtures
At present, almost all the time, admixtures are used for all the concreting work. It adds more advantages.
With the current developments in this industry, there are admixtures that can provide multiple functions such as retarding and water reducing actions.
As we know, superplasticizers are widely used as admixture due to its advantages. These admixtures are categorized under chemical admixtures.
Superplasticizers reduce the water requirement by 15 to 20% without affecting the workability leading to high strength and dense concrete. This strength increase will be for the same cement content with the reduction of the amount of water.
Further, we can reduce the cement content by adding a superplasticizer to keep the required strength. By that, we can save some money.
However, the dosage of the admixtures shall be as specified by the manufacturer.
Overdosage could reduce compressive strength also.
8. Compaction of Concrete
It is quite clear that compaction directly affects strength.
Poorly compacted concrete has less strength as shown in the following figure.
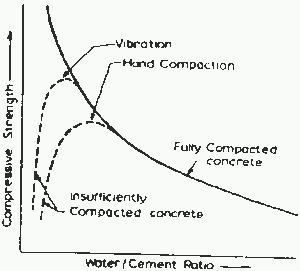

Poorly compacted concrete has more voids and as a result, it reduces the bond between the aggregates.
Therefore, it is very important to compact concrete adequately.
9. Time After Concreting
The age of the concrete is an indication of the strength development of concrete.
With time concrete strength increases but it does not increase proportionately.

Time is the main factor that reflects the strength of the concrete. When the concrete getting older, its strength increases. However, beyond a certain period, the increase of the strength is minimal.


