A structural engineer should be aware of answering the question of how to select concrete grade.
Selecting a suitable concrete grade which also can be identified as selecting the correct characteristic strength of concrete is a challenging task. Further, it is also required to select the correct concrete gade for an economical desing.
As we know, the strength of the concrete, rebar and section dimensions, etc are the key factors affecting the element structural capacity. Therefore, we need to select the correct/appropriate concrete gade.
Let’s discuss how to select concrete grade. This discussion is based on the British Standards.
Initially, when the BS 8110 is used for the design of reinforced concrete structures, the selection procedure can be outlined as follows.
- Adequacy of stretch for the limit state (SLS and ULS)
- Durability Requirements (as specified in BS 5328-1:1997 and BS 5328-2:1997
- Other special requirements.
BS 8110 and BS 5328 consider the durability requirements for specifying the concrete required to design and accordingly the cement content and water-cement ratio are selected.
However, later development of the standards, Eurocode 2, BS EN 206, etc consider more detailed durability requirements when specific to the concrete.
The selection of the concrete gade is based on the exposure condition of the structure.
The further development of the British Standards has a more precise answer for the question How to select concrete grade. Let’s see the what are the standards available to specify the concrete.
- Basic standard Eurocode 2 will be referred for the durability requirements and limit state strength
- BS EN 206:2013 – Concrete – Specification, performance, production and conformity.
- BS 8500-1:2015+A1:2016 which is a complementary British Standard to BS EN 206.
Let’s see what are the new British Standard(BS 8500-1:2015+A1:2016) guidelines for specifying concrete.
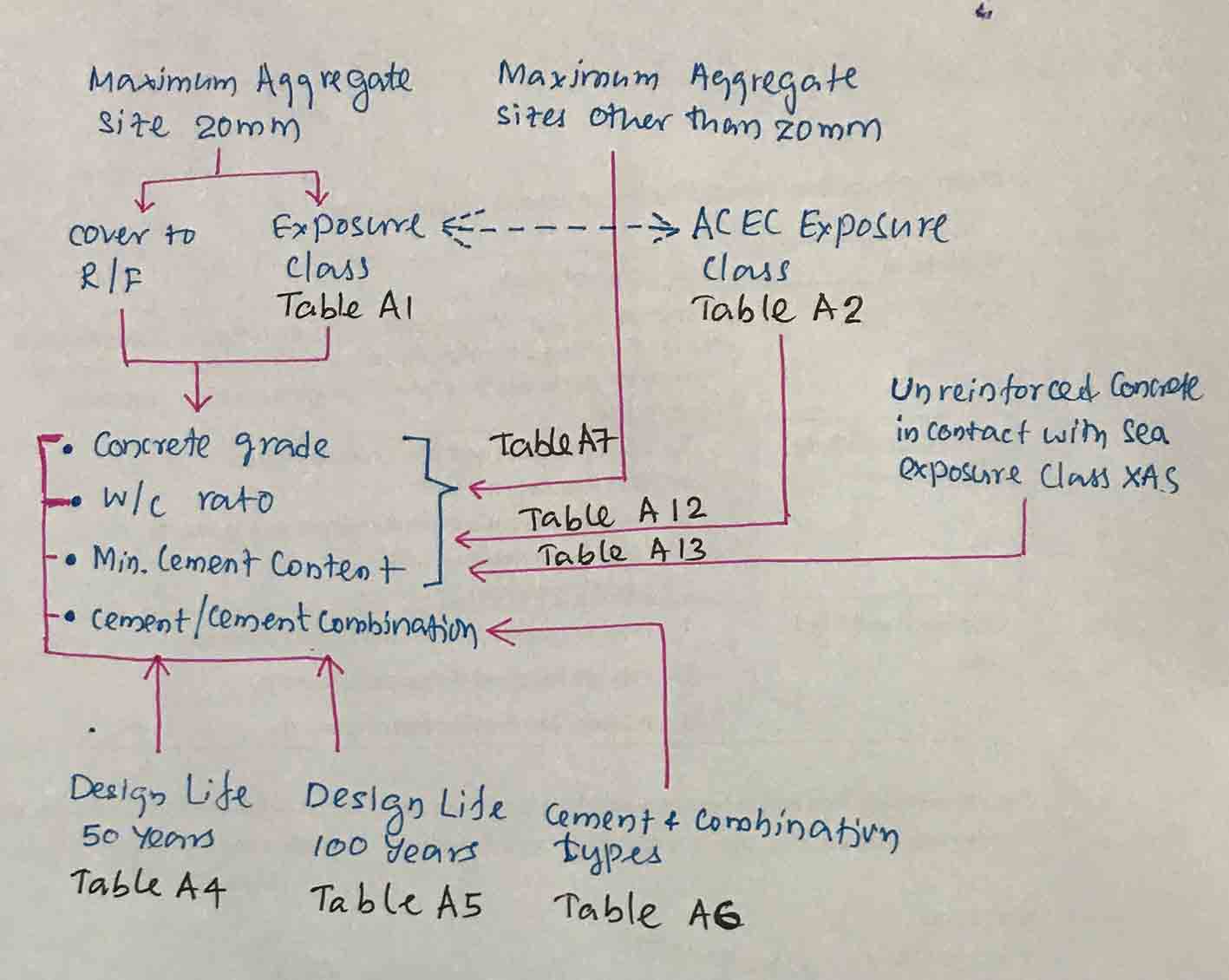
- Firstly, find the exposure condition that the structure is exposed. Accordingly, find the exposure class from Table A.1 of BS 8500-1:2015+A1:2016.
- Further, Table A.2 shall be referred for Aggressive chemical environment for concrete (ACEC) exposure classes. ACEC class shall be selected based on sulfate content, magnesium content and pH value when these chemicals are observed in the groundwater.
- Table A.4 and Table A.5 shall be referred for the concrete grade, water-cement ratio and cement content for design life 50 years and 100 years respectively. These tables cover only the concrete with a 20mm maximum aggregate size.
- Selection of the concrete is made based on the exposure class and the nominal cover to the reinforcements.
- In this process, Table A.6 – Cement and combination types, Table A.7-Minimum cement and combination contents with maximum aggregate sizes other than 20mm,
The following chart may be referred to for further clarification on the process of selecting concrete grade, cement content, water-cement ratio, cement/cement combination, and minimum cement content according to BS 8500-1:2015+A1:2016.