How to prevent corrosion? What are the practical methods that can be applied and what are the alternatives available? Let’s discuss in detail this issue as it is quite important to know if we are involved with steelwork.
Firstly, let’s see what are the consequence of steel corrosion?
From the first date we expose the steel to a corrosive environment, it stars the deterioration process. Initially, it is a very slow process and we do not notice it till it develops to a certain extent.
It starts changing the colour as the initial sign.
The following figure indicates the simple descriptive service life model for reinforcement steel. The same could be used for the other steels.
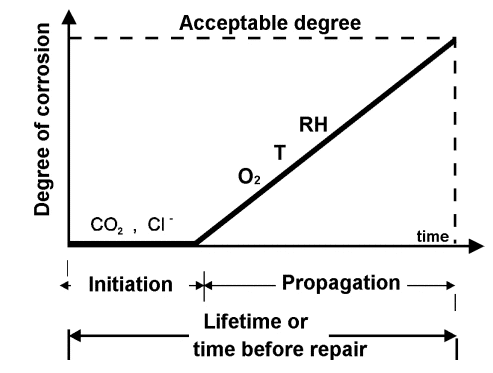 Where, T – is temperature and RH – is relative humidity
Where, T – is temperature and RH – is relative humidity
- Initiation
Initiation is the stage where it consists of time for erection until the aggressive agent reaches the steel and depassivates the steel. The aggressive agent could be chloride or carbonation front.
- Propagation
Propagation is the period from the depassivation until a certain acceptable level of deterioration is developed in the structure.
Lift time or the time before repair shall be kept in mind when we work with the steel as it is quite vital and lack of attention could lead to severe issues and additional expenses.
How to Prevent Corrosion?
Let’s discussed the available methods for protection from corrosion. Corrosion prevention of rust prevention shall be attended to as discussed above within the time before repair.
So that we can have a better performing structure.
The following actions and use of material could avoid/minimize the risk of corrosion.
- Metal Types
- Protective Coatings
- Environmental Measures
- Sacrificial Coatings
- Corrosion Inhabitors
- Design and Detailing
- Maintenance
Let’s discuss each type that can be used to prevent corrosion.
Metal Types
Whenever possible it is advisable the use steel that is not subjected to corrosion.
Metals like aluminium and stainless steel could be used as alternative materials.
The cost factor and the strength of the material need to consider when these alternatives are selected.
For example, if we are building a bridge, we won’t be able to use aluminium or stainless steel to replace structural steel. However, if we are constructing a simple roof that does not have larger spans, we could use the aluminium frame to support the roof.
Protective Coating
Mainly there are two types of protective coatings that can be used for rust prevention.
They are
- Painting
Painting acts as a protective barrier to the steel and avoids steel exposure to the environment.
The application of paints is a vast subject which needs a detailed study. However, let’s briefly discuss it.
Depending on the nature of the structure and where it is to be constructed, the specification for painting is made. For example, different specification is used for marine structure and structures to be constructed away from the sea.
The risk of corrosion is very higher very close to the sea and need higher protection. However, when it is constructed in the middle of the country, we do not need to that strick on the selection of the paint.
Further, an internal structure that does not widely open exposure to the environment could not need much tough specification to protect the steel.
The number of coating applied to the steel is one of the governing factors for protection. Therefore, the lesser the risk, we could limit the number of coatings.
- Powder coating
Powder coating is a kind of membrane created on the steel surface. The following steps are followed in the application of powder coating.
-
- Clean the metal surface
- Apply dry powder
- Metal is heated and powder fuses into a smooth continuous film
- Different powder compositions can be used.
- Composition could include acrylic, polyester, epoxy, nylon and urethane
Environmental Measures
It is the most suitable and sustainable method to be employed to protect the steel. But we cannot always protect the structure by using this method.
We have to have exposure when they are used in construction and at service.
In general, internal elements are less prone to corrosion due to a lack of ingredients for corrosion.
If covered adequately, the presence of moisture and oxygen together is minimal.
For example, when we build a structure close to the sea, minimizing or avoiding sea breeze entering into the building will reduce the corrosion.
Sacrificial Coatings
The name itself provides an idea about the coating. It is a type of metal coating applied to the steel. It could mostly be in the form of oxides.
There are two methods of applying sacrificial coatings
- Cathodic Protection
Though the name is not that familiar to us, this is the well-known method of galvanizing. It is the process of coating steel with zinc. Further, the zine is more active than steel it helps the process quite easily.
This method is widely used in the world as it is more reliable and durable.
The articles hot-dip galvanizing and galvanizing vs painting, discuss on galvanizing to protect the steel from corrosion.
Steel pile lines, structural steel, offshore structures, ship hulls, etc, are protected from rust by this method.
- Anodic Protection
Application of less active metal such as Tin on the steel alloy is anodic protection.
As tin is not corrosive material, steel will be protected until the applied Tin layer is on the steel surface.
Anodic protection is widely used in a situation where cathodic protection cannot be done.
Further, it is mostly used for carbon steel storage tanks.
Corrosion Inhabitors
Corrosion inhibitors are chemical that reacts with the steel surface or surrounding gases to avoid corrosion.
They form a membrane on the steel surface to protect it exposing to the environment.
Inhabitors can be applied as a solution or coating or gas to the steel to form the protective film.
The Wikipedia article Corrosion Inhibitor could be referred for further information.
Design and Detailing
Structural and architectural design plays a major role to prevent corrosion, and they shall know how to prevent corrosion.
The method of detailing the structural element shall be done in a manner that it does not encourage corrosion.
The following key aspect can be highlighted.
- Adequate access
The design shall allow adequate access for periodic maintenance. If we cannot reach to the structure due to any reason, no inspection and no maintenance can be done.
If it is not possible to provide access with conventional methods, it shall be planned during the design and necessary modification or arrangement shall be done in the planning and design stage.
- Collection of Dust
The design could plan to avoid collecting dust in the steel elements. Even though we have applied protective coatings, their durability highly depends on whether they are dried or wet.
Having moisture with dust is a good environment to start the rust. Therefore, we shall attend to prevent rust formation.
- Air Movement
Attentions hall is made to avoid stagnating the air. Once the chlorides present with moisture, it is like asking to corrode.
Therefore, adequate circulation could avoid such issues.
- Openings
We cannot build anything without an opening.
We need to access what we were built. As we built to use.
However, it is recommended less number of openings to avoid entering the ingredient to the corrosion with air.
If there are openings in the roof or close to the roof, moisture, chloride, etc could come into the building. If the building is located close to the sea and when there are dominant openings in the direction of the wind (facing to wind), the risk of corrosion is very high.
These issues shall address from the preliminary design level and avoid as much as possible to prevent corrosion.
- Regular Inspections
It is recommended to monitor the steel structures regularly to know their condition.
Regular inspection for a schedule could be done to identify whether there are issues connected with the durability of the structure.
If notice such an issue, actions can be taken at the initial stage before it becomes worst.
Maintenance
Periodic maintenance is a must for steel structures whether it is galvanized and painted or painted or we use any other method discussed above to avoid corrosion.
After inspecting the structure periodically, necessary maintenance work shall be done.
Avoiding maintenance work could increase the severity of the defects and it will reduce the durability of the structure.
Further, not having done the regular maintenance work will increase the cost of repair the defect at the latter stage.
In addition, notification on how to prevent corrosion to the maintenance team could alert them.


