Retaining wall types and their behavior is discussed in this article. Different classifications of retaining systems are also discussed.
Why do we need a Retaining Wall?
Any structure that is used to retain the earth is generally called a retaining wall. There are other types of retaining structures that retain materials like rock, sand, etc.
The design of retaining structures is not same for the all types of structures. It depends on the structural behavior and forces acting on a retaining wall.
Types of Retaining Walls
- Gravity [ masonry, stone, concrete, etc.]
- Semi Gravity
- Cantilevered/Propped
- Counterfort/Buttressed
- Diaphragm Wall
- Anchored
- Piling [ sheet pile, bored, secant, tanget]
Let’s discuss each type in detail.
Gravity Retaining Wall
As the name implies, the structure bears the load by the gravity load. In other words, the self-weight of the structure act as the counterweight to bear the applied overturning moment.
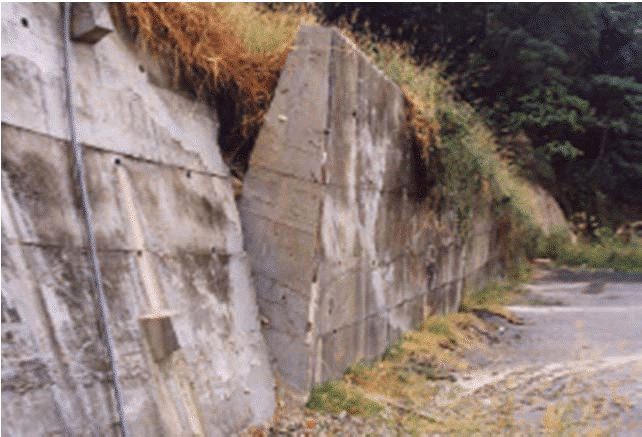

There are different materials used for the construction of retaining structures. Masonry and stone were used for construction early days.
However, with the development of the construction industry and after starting using concrete, concrete gravity retaining walls have become more popular.
In general, gravity retaining structures are constructed as mass concrete structures. However, in some situations, nominal reinforcement is provided as a measure to avid the thermal cracks.
The gravity retaining structures are mostly observed in the construction of hydraulic structures.
Semi Gravity Retaining Structures
This is a further development of gravity structures. In a gravity structure, generally, we do not provide rebar to carry the load.
However, in semi gravity structure, we provide a certain amount of reinforcement to carry the developed tensile stresses in the surface where the soil pressure is applied.
When there are larger forces applied and limitations in increasing the with of the retaining wall, reinforcement is provided with modified based to maintain the stability.
Cantilever Retaining Wall Propped Retaining Wall
Cantilever-type walls are the most common type of structure we observed in the construction. They are generally reinforced concrete structures.
This type is the most effective type when there are limitations in the space. We can reduce the thickness of the wall with the reinforcements provided for the wall and the foundation.
The proper retaining wall also is the same as the cantilever retaining wall. The only difference is providing support at the top level to control the later deflection at the top.
Not like a cantilevered retaining wall, propped cantilever wall is more stable.
Counterfort and Buttressed Retaining Wall
Both types of retaining walls are used when the retaining height of all increases.
When the height of the free cantilever wall increases, its dimensions and reinforcements needs to be increased. This will not be economical when the wall height is considerably higher.
For example, at heights like 7m-15m, we may consider building additional stiffness to reduce the stresses on the main wall.
Further, more importantly, the construction of counter for and buttressed retaining walls does not lead to improving the stability of the wall. Only the increase in the self-weight due to the diagonal walls, contribute to enhancing the factor safety against overturning.
- Counterfort Retaining Wall
The name implies the arrangement of the stiffener walls. There is counterfort in the wall improve the wall stiffness.
The stiffener walls are placed where the earth pressure is applied in this type of wall.
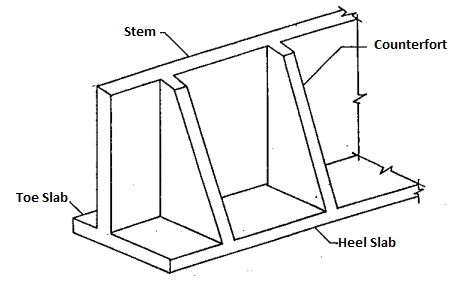
The counterfort wall is not that effective as the buttressed retaining walls as the counterfort is in tension. When the element is tension, we have to provide adequate reinforcement to carry the loads.
The counterfort can be in different forms. It is always not required to construct converting the total wall height and the foundation width. There may be smaller counterfort that acts effectively on reducing the wall bending and shear forces.
- Buttressed Retaining Wall
Buttressed walls also provide similar support to the main wall in reducing the bending and shear forces.
However, it is more efficient when compared to the counterfort walls as in this type, the concrete in compression. Concrete is more efficient in carrying compression forces.
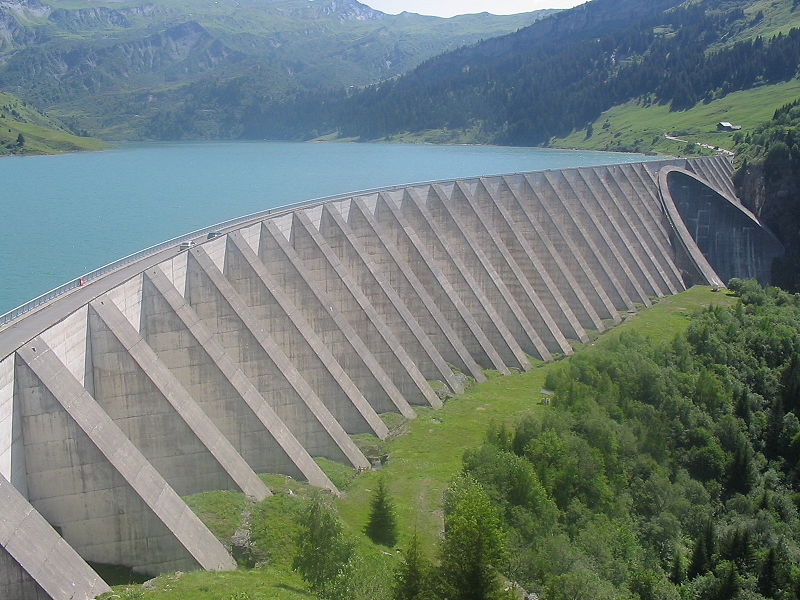

The stiffener walls are located outside. When there is a space in the outside area and is free to construct the stiffener walls, this option is more economical.
Diaphram Wall
These types of walls are new inversion in the construction industry. The construction method is more similar to the cast-in-situ bored piles.
Diaphram walls are constructed as replacements to the retaining walls constructed as sheet pile walls, secant pile walls, etc. The same wall can be used as the basement wall after the construction.
The diaphragm walls are now more popular in deep basement construction.
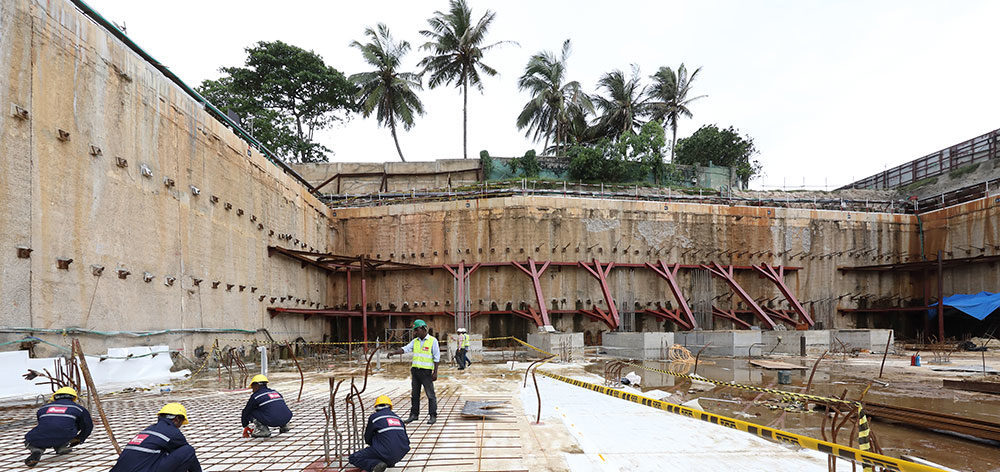

Diaphram wall could be constructed as a free-standing wall that can bear the lateral loads by itself. In deeper basement construction, a diaphragm wall may be constructed as an anchored wall or propped wall.
Anchored Walls
Providing lateral restrain to the retaining wall to maintain stability is one of the commonly used methods in taller retaining walls.
When the height of the wall increases, we have to increase the thickness of the wall. If lateral restrains are provided at regular intervals, we can reduce the cost of the wall.
Providing lateral restraints can be observed on different occasions.
- Provide lateral restrain for concrete walls.
- Provide lateral restrains for sheet pile walls
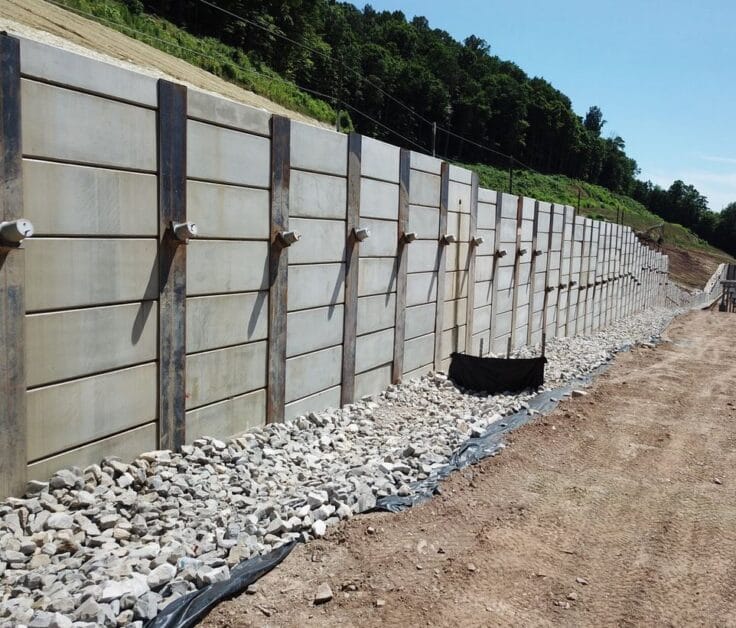

Generally, the termination of the anchors is done beyond the failure line having the required factor of safety.
Piling Retaining Walls
Piling methods are commonly used for retaining the earth in deep basement structures.
Though it will take a certain time to establish the retaining system, the piling method is more reliable. Further, it can carry a comparatively higher load when compared with a sheet pile wall.
There are different types of piling walls.
- Sheet Pile walls
- Bored pile walls
- Secant pile walls
- Tangent pile wall
Piling retaining walls are constructed as anchored walls also.
In addition to the above types of retaining walls, there are other methods of retaining the earth.
The most common systems available can be discussed as follows.
- Soil Nail Walls
- Soil Strengthening
- Gabion meshes
- Mechanically stabilized earth retaining walls
- Crib wall
Let’s discuss each category in detail.
Soil Nail Wall
It is a kind of earth retaining system that is more commonly used as a slope stabilization method. It prevents the lateral movement of the earth more effectively.
We can see this method more commonly in road construction.
Steel road anchored into the deep soil layer is done in the regular grid as per the design requirement. These points are connected by reinforced concrete beams.
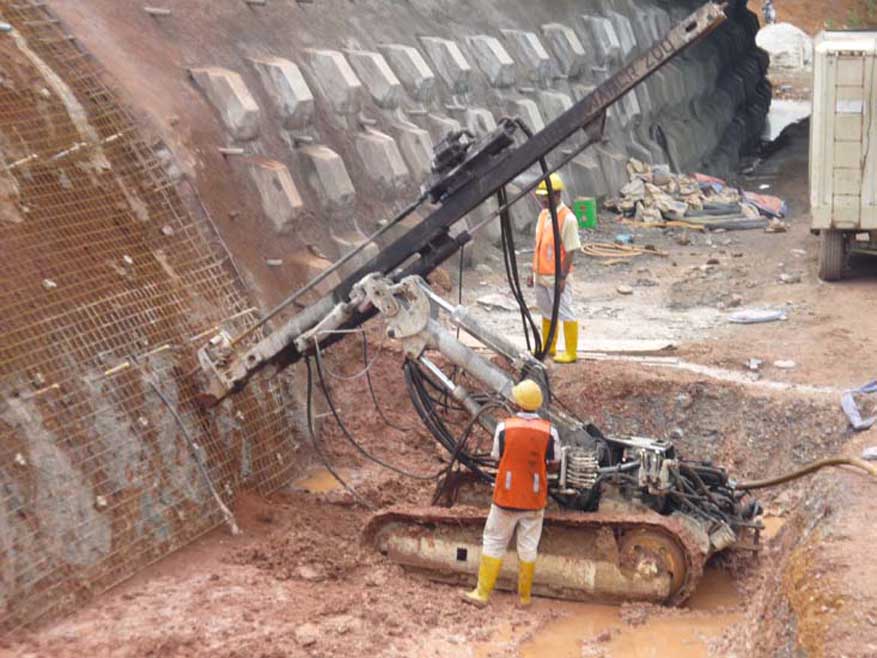

The area covered by the beams will be covered with shotcrete concrete placed with mesh. There may not be beams always to connect anchoring points.
Gabion Wall
A gabion wall is not only a retaining wall. It has many uses as follows.
- Used as temporary flood walls
- Channel lining
- Stepped weir in flood control
There is no development in the pour water pressure as it releases the significant later force.


