Concrete shrinkage is inevitable under normal circumstances unless we use a special type of cement for the construction. Nonshrink concrete made using the cement that there is no volume reduction after pouring could be the only solution for this.
However, in general construction, we cannot use nonshrink concrete due to the production of small quantities and as it is expensive to use.
Therefore, we have to face the issue the concrete shrinkage during the construction and necessary actions to be taken to minimize the impact on the durability of concrete.
What is Concrete Shrinkage?
Shrinkage is the change in volume over time in a way it decreases the dimensions of the concrete.
The volume of concrete changes during the hardening process due to the effect of hydration of cement and concrete drying process with the loss of water in the paste.
The reduction of the volume in a concrete covered with three sides occurs in the vertical direction by reducing the height of the concrete.
Types of Shrinkages in Concrete
Mainly there are six types of concrete shrinkages. Let’s list them.
- Plastic Shrinkage
- Chemical Shrinkage
- Autogenous Shrinkage
- Drying Shrinkage
- Thermal Shrinkage
- Carbonation Shrinkage
Plastic Shrinkage
Plastic shrinkage occurs on the surface of the fresh concrete due to the evaporation from the surface or by absorption from the concrete or bedding.
Also, it can be identified when the rate of evaporation is greater than the rate of bleeding in the concrete.
This very quick process and occurs in the first few hours of concrete pouring.
Fresh concrete moving towards each other in this process. Shrinkage in the surface layer prevents the movement of internal parts and it leads to developing tensile stresses in the fresh concrete.
When these tensile stresses are greater than the tensile strength of the fresh concrete, plastic cracks could appear.
These cracks would be wider about 1-2mm and 300 – 500mm long. The depth of the crack could be around 20-50mm.
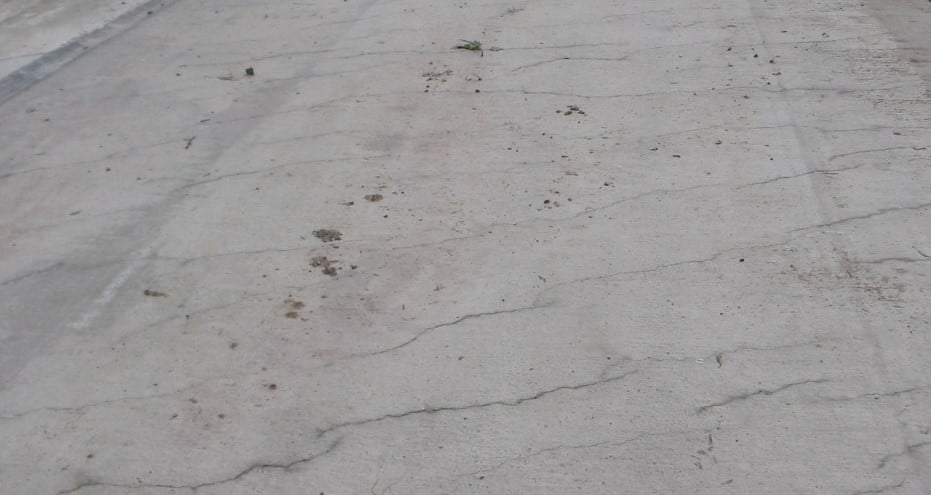

The main cause of the plastic shrinkage cracks is the evaporation of the water from the concrete surface. If this can be avoided, concrete shrinkage can be minimized.
The main thing we can do is the adequate and timely curing of concrete. The article methods of curing of concrete could be referred to for more information on curing.
In addition, attention shall be made to the curing time to avoid plastic shrinkage in concrete.
Chemical Shrinkage
There is a volume reduction in the concrete when the water chemically binding in the process of cement hydration.
Further, there are several chemical transformations in the cement paste in the hydration process. These actions reduce the volume of the concrete and it is called chemical shrinkage.
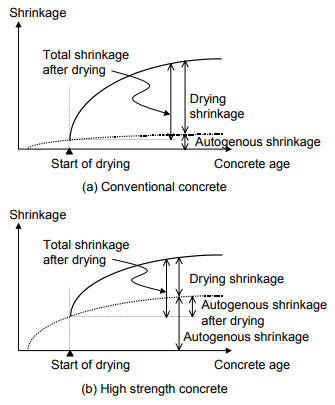
Autogenous Shrinkage
Autogenous shrinkage is also called hydration shrinkage as it directly relates to the user of pour water within the concrete for hydration reaction.
Further, there is no clear demarcation between the autogenous shrinkage and chemical shrinkage.
When there is no adequate moisture to carrying out the hydration reaction, swelling in the concrete occurs.
In this situation, withdrawal of water from the capillary pours for hydration reaction occurs and it leads to shrinkage of concrete.
The process of withdrawal of pour water from the capillaries for the hydration process is called the self desiccation.
Drying Shrinkage
Contraction of hardened concrete due to the loss of capillary water in the concrete is identified as drying shrinkage in concrete.
Drying shrinkage occurs in 3 -4 days or even after several months after concreting.
Thin members having a large surface area are susceptible to drying shrinkage cracks in concrete. More on the reasons for shrinkage will be discussed later in the article.
Drying shrinkage leads to cracking of concrete when the movement of the concrete retained by elements such as subgrade, foundation, part of the structures, etc.
Let’s discuss the factor affecting drying shrinkage.
Factors Affecting Drying Shrinkage
- Concrete mix design – excessive cement content, higher water content, etc affect the drying shrinkage.
- Addition excessive water at construction sites.
- inadequate reinforcement to carry the internal stress due to the internal restrains
- Inadequate curing of concrete.
- Lack of attention to control the evaporation of water form concrete surface
- Lack of contraction/expansion joints. Joints shall be provided as per the code requirements. The spacing of the joints shall be as per the section requirements and based on the provided area of reinforcements.
- The geometry of the concrete.
- Use of the chemical and mineral additives. Low dosage chemical additives do not affect the drying shrinkage of concrete. However, when a high dosage is used, it has a higher impact on drying shrinkage.
- Inadequate compaction of the concrete could cause shrinkage in concrete.
Shrinkage in concrete can be minimized if we attend to the above factors when applicable and as required.
Since the cracking of this nature is directly affecting the durability of concrete, the highest attention shall be made.
The following figure indicates the variation of drying and autogenous shrinkages.
 Thermal Shrinkage
Thermal Shrinkage
Thermal shrinkage is also known as the thermal contraction is a type of shrinkage in the concrete due to thermal movement of concrete.
The temperature of the concrete varies and when it rises concrete expands and when it lowering concrete shrinks.
If this continues in the concrete and when there are internal restrains in the concrete, concrete gets cracked due to the stresses developed in it.
Seasonal variation of temperature could lead to cracking of concrete that can cause as a result of the thermal contraction in the concrete.
Further, it could be due to the rise in the temperature during the hydration process.
Carbonation Shrinkage
Carbonation shrinkage occurs due to the carbonation of concrete.
Carbonation of a process of deterioration of concrete that leads to corrosion of the reinforcements. It occurs by the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere creating with the hardened concrete.
In this process, concrete weight increases while its volume is reduced. This causes concrete shrinkage.
Let’s discuss some of the important factors affecting all types of shrinkages.
Factors affecting the Shrinkage of Concrete
Let’s discuss the major factors that need to be controlled to avoid/minimize shrinkage.
- Lateral Restrains: Restrain in the concrete is due to the foundations, part of the structure, etc. This can be controlled by providing regular contraction joints in the concrete. Adequate expansion joints will also minimize the cracking of concrete due to the reduction in the lateral restrains.
- Relative Humidity: This is a well-known fact that the relationship between relative humidity and evaporation.
- Elastic Modulus of Aggregates: Higher the modulus of the aggregate less the possibility of cracking or shrinkage.
- Water Cement ratio: Cement content, water content directly affect the shrinkage. Higher the cement content higher the shrinkage.
- The geometry of the Concrete element