Soil cement stabilization is a soil stabilizing technique that is used for building structures. The technique involves mixing cement and soil to make a mixture that can be used for construction purposes.
The process of soil cement stabilization starts with the removal of any vegetation on the site and then the ground is compacted with heavy equipment. This will allow any air pockets in the ground to be eliminated. Then, the site is leveled before adding a layer of gravel which will help drain water away from the area. Next, an impervious membrane should be laid down to prevent water from seeping through into the gravel layer.
Finally, a mixture of cement and soil is added up to two feet deep depending on how deep you need it for your project. This mixture has been mixed in a ratio that will allow it to harden quickly without too much cracking or shrinking over time.
Let’s see a comparison of soil cement stabilization with another method of stabilization. Source: Internet
| Pretreatment | Technological Maturity | Economic Efficiency | Secondary Pollution | Mass Addition | Evaluation of Project Adaptability |
| Cement solidification | Good | Good | Slight | Great | Combined with other methods |
| Hydraulic waste solidification | Better | Good | Slight | Tremendous | Feasible |
| Thermoplastic material solidification | Better | Weak | Slight | Great | Infeasible |
| Phosphate stabilization | Good | Good | Slight | Slight | Combined with other methods |
| Ferrous sulfate stabilization | Normal | Better | Slight | Slight | Infeasible |
| Sulfide stabilization | Better | Worse | Normal | Slight | Infeasible |
| Polymeric chelant stabilization | Good | Better | Slight | Slight | Feasible |
Why We Need Soil Stabilization
To assure the finest construction, durability, and safety, a structure or roadway needs to have a solid foundation. The foundation itself needs to be supported by solid ground capable of dispersing the full weight of the structure. If the soil is unstable, immediate settlement or time-consuming settlement could have detrimental effects.
Soil stabilization is done before construction on more than simply buildings. Other soil stabilization techniques may be used when building new roads, overpasses, parking lots, and even airports. As the soil expands or deforms excessively, it can weaken the pavement and lead to fractures and bumps that could eventually be harmful. Any obvious deterioration of a road can quickly cause an accident. The effects can be far more disastrous, risky, and expensive on a runway.
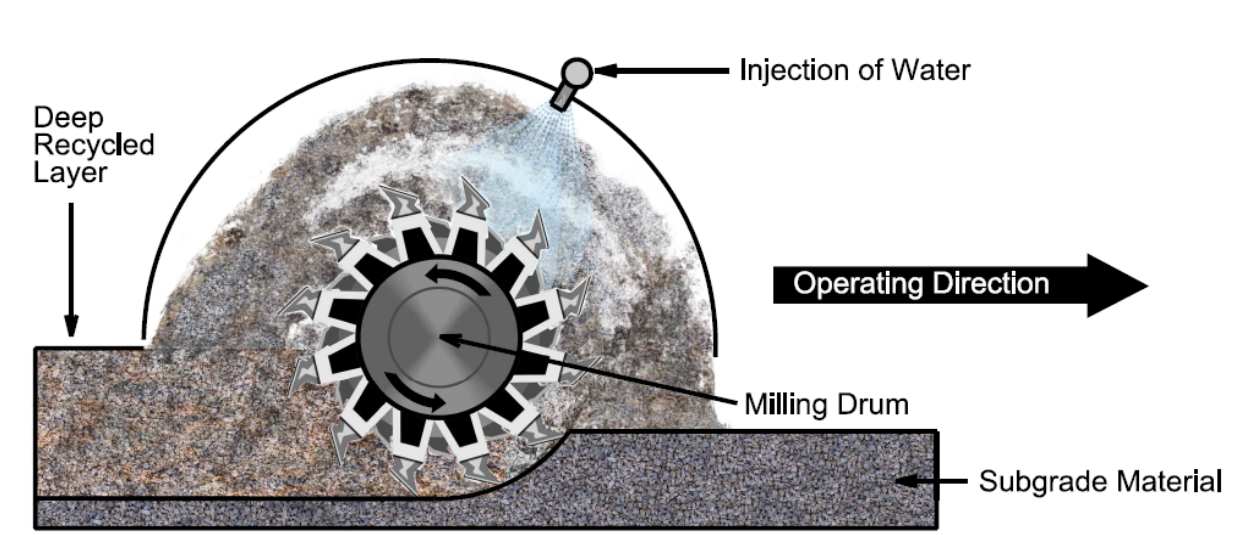
Different Types of Soil Cement Stabilization Options
There are different types of soil chemical stabilization methods. Some of them are as follows.
- Lime and cement soil stabilization
- Fly ash soil stabilization
- Polymer stabilization
- Soil stabilization with geotextiles
Deep mixing and surface mixing methods are the two main methods of chemical stabilization. Further, we and dry mixing methods can be used for deep mixing. The article soil stabilization could be referred to for further information.
In this article, we are concentrating on cement stabilization methods.
The soil-cement stabilizer is a device that stabilizes the soil using cementing. There are many types of soil cement stabilization options, and they are classified into two types;
- Natural soil stabilization options
- Cemented soil stabilization options
Factor Affecting Cement Stabilization
- Type of soil
Granular soil is preferred for cement stabilization though it can apply to other types of fine soil as well. However, soil having low permeability or resistance to the mixing would be much more difficult especially when we are doing the deep mixing and grouting methods.
- Cement requirement
It is required to use a significant amount of cement quantity for this process.
- Water quantity
The quality of water to be mixed with is very important. Therefore, we shall be well aware of the condition of the water to be used for this purpose.
- Mixing, compacting and curing
Mixing, compacting, and curing are very important in this process, and strength development is depending on having good control over these aspects.
- Admixtures
Cement itself contains some significant admixtures that aid in the formation of a strong bond. When cement and water react, these additives play a crucial function.
Advantages of Soil Cement Stabilization
Some of the important facts about cement stabilization are as followings.
- Improve the strength of the soil
- Improve the waterproofing qualities of the soil
- Can be used to create a platform for project execution
- Can control the swelling properties of the soil
- Improve the durability
- Soil stabilization reduces the cost compared to other options we have.


![Tunnel Design [a guide to designers]](https://www.structuralguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Tunnel-1-1024x599.jpg)