Soil stabilization is a technique used to improve the condition of the ground to have a higher bearing capacity by modifying the engineering properties of soil.
Soil stabilization methods adopted in the construction industry are discussed in this article. It is a process of improving the engineering properties of the soil by means of mechanical and chemical methods.
Ground improvements are required when a structure is required to build in weak soils. Depending on the soil types the improvement methods are different.
Let’s see
What is Soil Stabilization
- Soil stabilization is the ground improvement.
- Initially, the condition of the ground is assessed by visual for shallower depth and by borehole investigation for deeper improvement. When there is no information on the condition of the ground, the common practice is to carry out soil investigation.
- Based on the borehole investigation /soil investigation results, suitable soil stabilization techniques are selected.
What are the advantages of Soil Stabilization?
- Soil stabilization improves the soil shear strength and compressive strength
- It reduces the soil compressibility as result it could reduce the settlements
- Reduce the permeability of the soil
- It is an environmentally friendly process most of the time.
Purpose of Soil Stabilzation
- Usually, the soil naturally has considerable shear strength and compressive strength.
- However, there are types of soils that do not have adequate strength to carry the applied loads.
- This could be at a shallower depth or deep level.
- In order to improve the condition of the soil, soil stabilization method are used.
- Ground improvement could be done mechanically or chemically. In addition, there are other soil stabilization methods such as biological stabilization, etc.
Soil Stabilization Methods
The two main soil stabilization methods are discussed in detail in this article.
- Mechanical Stabilization of Soil
- Chemical stabilization of Soil
Both of the methods were used in accordance with the condition of the ground and after assessing the ground profile by a borehole investigation.
Chemical Stabilization of Soil
Chemical soil stabilization techniques are not common when compared to mechanical soil stabilization methods. The mechanical methods are not required very high skill whereas chemical soil stabilization techniques required sophisticated technologies and technical knowledge.
Stabilization of soils such as silt, clayey peat, peat, organic soils, etc. is done.
Let’s see what are the most commonly used materials that can be used for ground improvement.
- Cement
- Lime
- Fly-Ash
- Blast Furnace Slab
- Pozzolans
- Bitumen
- Polymer
All these materials are mixed with the soil and stiffness or the strength of the soil is enhanced. The process of stabilizing with these materials will be discussed in the latter part of this article.
Mainly there are two types of chemical stabilization of soil.
- Surface Mixing
- Deep Mixing
Surface Mixing
Relatively easy method this can be done from the shallower depth to deeper level. The mixing of the stabilization material is done with the soil using a machine.
Removal of the soils which are highly organic and or highly compressible other silts such as peat could be done before the mixing.
Deep Mixing
As the name implies, the deep mixing method involves depths greater than 1.5m generally. This method can be used to stabilize the solid for larger depths.
Weaks soil types such as clay, peat, or organic soils will be mixed with stabilizer injected into the soil by mechanical means.

Mainly there are two approaches in the deep mixing method.
- Wet mixing
The soil will be mixed with slurry binding (cement, lime, fly ash, etc).
This method is greatly applicable for soils having a moisture content of less than 60%. Higher the moisture level, the lesser the effectiveness of mixing.
- Dry Mixing
The soil is mixed with the dry binder.
This type of mixing is applicable for soils having higher moisture content such as above 60%. Since the dry binder is inserted to mix with the soil, it mixes properly with the presence of moisture.
Deep mixing is done to stabilize soils to a deeper depth. In this process, stiffening and strengthening of soil will be done in regular intervals. Soil mass will be stiffened like piles in regular spacing. These stabilized soil piles will carry the applied loads.
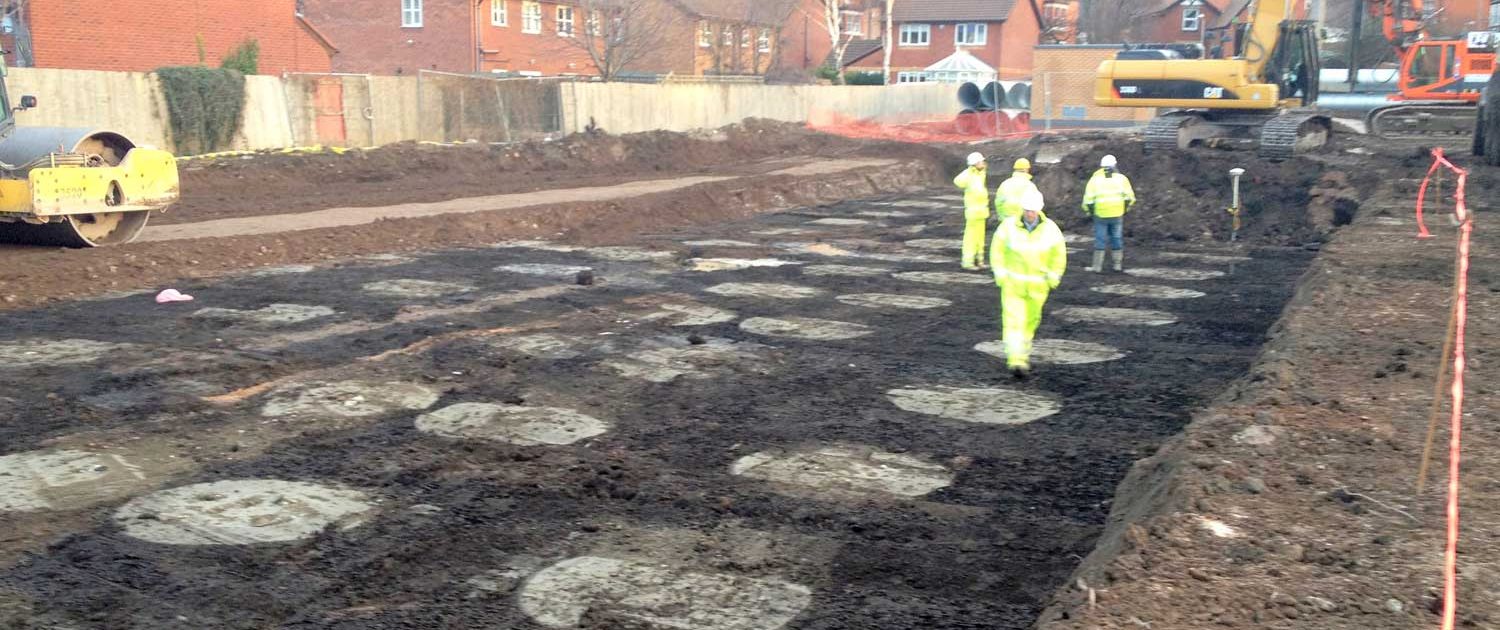

The desing of these stabilized earth stabilized columns depend on the following factors.
- Stabilizer Design
- Type of binder used for the stabilization and its chemical properties
- Water binder ratio. It greatly affects the strength of the stabilized pile.
- Binder Content
- Geometric Design
- Length of the column or the depth to be cast as stabilized earth column
- Diameter of the column
- Spacing between the columns
- Orientation of Columns (as blocks, signed columns at regular spacing, columns connected each other and placed in lines, regular orientation.
Factors affecting the strength of stabilized soil
The following factors could be considered vital in the development of the strength and stiffness of the stabilized earth.
- Organic matter
- Sulfates
- Sulfides
- Compaction
- Moisture content
- Temperature
- Wed dry effect
Mechanical Stabilization of Soil
Though the name implies mechanical stabilization, we do not always use mechanical means to stabilize the soil.
Simply, we change the grade of the material with stabilization. A more arrange or more cohesive mix is created by applying pressure on the soil layers. Due to the compressibility, the density of the soil increases.
The application of the load would depend on the magnitude of loads to be applied on the soil at the service stage.
There are three main mechanical soil stabilization methods.
- Compaction
- Preloading
- Replacement
- Soil Reinforcements
Let’s discuss each of them in detail.
Compaction of Soil
It is the mouse commonly used method in the construction and convenient method.
This method is mainly used for granular soils that do not have adequate engineering strength parameters.
The following methods are used to compact the soil.
- Vibration
- Impact
- Kneading
- Pressure
The compaction of the soil is measured by means of the increase in density. To achieve better compaction, the moisture content of the soil is maintained at the optimum level.
The most commonly used method of measuring the compacting of soil is
- Proctor Dry Density
- Sand Cone Test
- Rubber Balloon Test
- Nuclear Density Test
There are special compaction methods such as dynamic compaction of soils. For more information, the article Ground improvements could be read.
Preloading
Preloading is kind of method that is used to apply a similar or higher pressure on the soil to achieve the settlement before the service stage. During the construction stage, a soil weight is added to the area the construction is to be done till the settlement is stable to a certain extend.
This method is mainly used for compressible soils such as peat, soils having higher organic content, and clayey soil that causes the consolidation settlement.
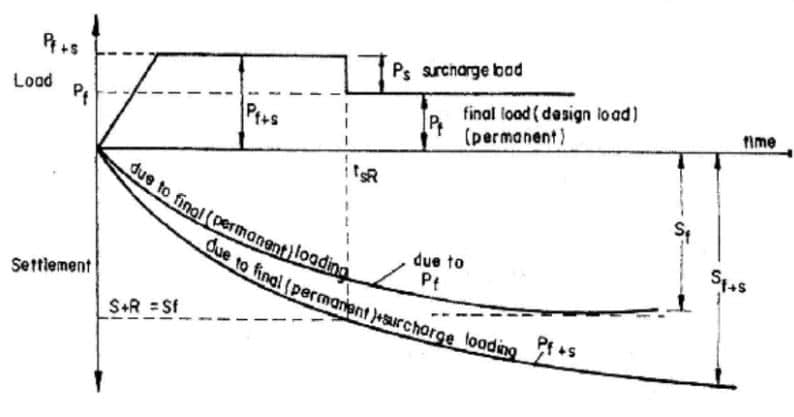
Let’s discuss the preloading process as a ground improvement technique.
- Since the loads to be applied during the service are known, the possible settlement can be estimated.
- Sine the preloading is a time dependence process, it is required to calculate the load to be applied to get the expected settlement.
- We can increase the load to reduce the loading time. This can be evaluated by the consolidation settlement calculation.
- After loading, the settlement of the ground will be monitored. Preloading could be kept till the ground settlement is reached its maximum. Further, monitored values can be compared with the computed values to reach a conclusion.
Replacement
Replacement of soil is commonly adopted for shallower depth when compared to the other soil stabilization methods.
Weak soils such as organic soils, medium and soft clay, etc. will be replaced with soil having good engineering properties. The most commonly used replacements are as follows.
- Gravel
- Sand
- Quarry Dust
- Crushed Stone
Other soil stabilization methods
- Geotextiles
- Recycled waste products
- Geomaterials – geogrids, geoblankets
- Soil Nailing
- Retaining Wall
The summary of the soil stabilization methods is elaborated in the following figure.




![Tunnel Design [a guide to designers]](https://www.structuralguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Tunnel-1-1024x599.jpg)