In the realm of structural engineering and design, the analysis of dynamic loads is a critical aspect that cannot be overlooked. One such method used to investigate the behavior of structures subjected to time-varying forces is time history analysis. This powerful technique allows engineers to accurately assess the response of a structure under the influence of real-life dynamic events, such as earthquakes, windstorms, or industrial vibrations.
What is Time History Analysis
Time history analysis is a numerical simulation method employed to predict the dynamic response of structures by considering the actual time-varying loads applied to them. Unlike simplified static analysis, which assumes that loads act instantaneously and remain constant throughout, it takes into account the changing nature of forces over time.
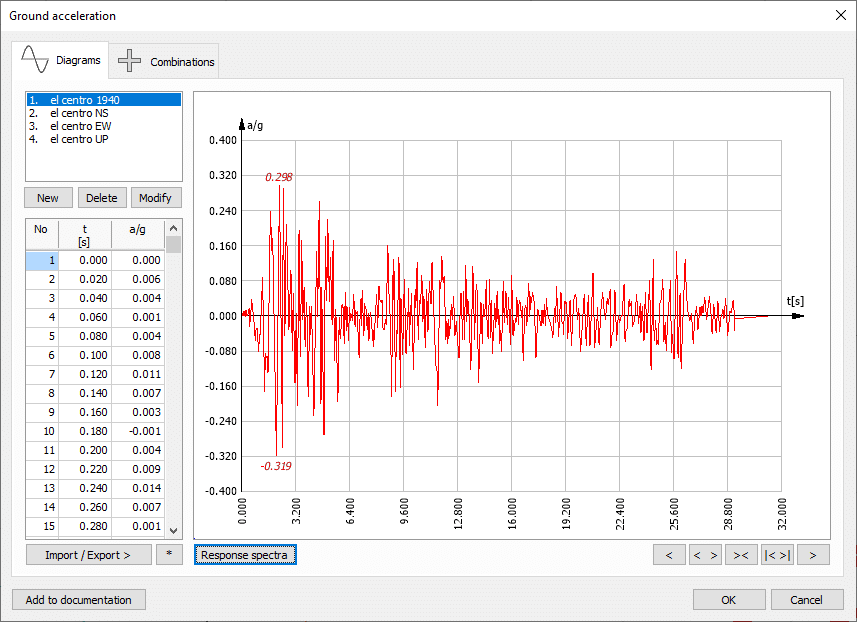
The most challenging part is the development of the time history curve for the analysis. Variation of the ground acceleration is required for the analysis. This would be able developed for the countries having the adequate data. However, the countries those does not have the experience in the earthquakes, they would have to use the curves developed by the other countries.
The Process of Time History Analysis
To perform time history analysis, engineers follow a systematic approach that involves several key steps. Let’s take a closer look at each stage of this process:
- Defining the Dynamic Loads: The first step in this type of analysis is to identify and characterize the dynamic loads that the structure will be subjected to. This may include seismic records, wind profiles, or other relevant time-varying forces.
- Developing a Mathematical Model: Next, engineers create a mathematical model of the structure using sophisticated software tools. This model should accurately represent the physical properties and behavior of the structure under consideration.
- Selecting Time History Records: Time history analysis relies on recorded data of actual dynamic events. Engineers carefully choose suitable time history records that closely match the characteristics of the expected loading conditions. These records are then applied to the mathematical model.
- Simulating the Structural Response: Once the dynamic loads have been applied, the software performs a numerical simulation to predict the structural response over time. This involves solving a set of differential equations that govern the motion and equilibrium of the structure.
- Evaluating Structural Performance: The analysis results provide valuable insights into how the structure behaves under dynamic loads. Engineers assess various parameters, including displacements, accelerations, stresses, and internal forces, to evaluate the structural performance and identify any areas of concern.
- Optimizing the Design: Based on the findings of the time history analysis, engineers can make informed decisions to optimize the design and improve the structural response. This may involve adjusting material properties, modifying the structural configuration, or implementing additional reinforcement measures.
Advantages of Time History Analysis
It offers several advantages over simplified methods, making it a crucial tool in the analysis and design of structures subjected to dynamic forces. Here are some key benefits:
- Realistic Representation: By considering the time-varying nature of loads, time history analysis provides a more accurate representation of the actual behavior of structures. This enables engineers to better understand the dynamic response and identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Evaluation of Safety: Dynamic events such as earthquakes can pose significant risks to the safety of structures. Time history allows engineers to assess the performance of a structure under extreme loading conditions, helping them ensure its safety and durability.
- Design Optimization: Through time history, engineers can iteratively refine the design of a structure to enhance its performance. By evaluating different scenarios and considering the dynamic response, they can make informed decisions to achieve an optimal design solution.
- Compliance with Codes and Standards: Many building codes and standards require the consideration of dynamic loads in the design process. Time history analysis enables engineers to meet these requirements and ensure that structures adhere to the necessary regulations.