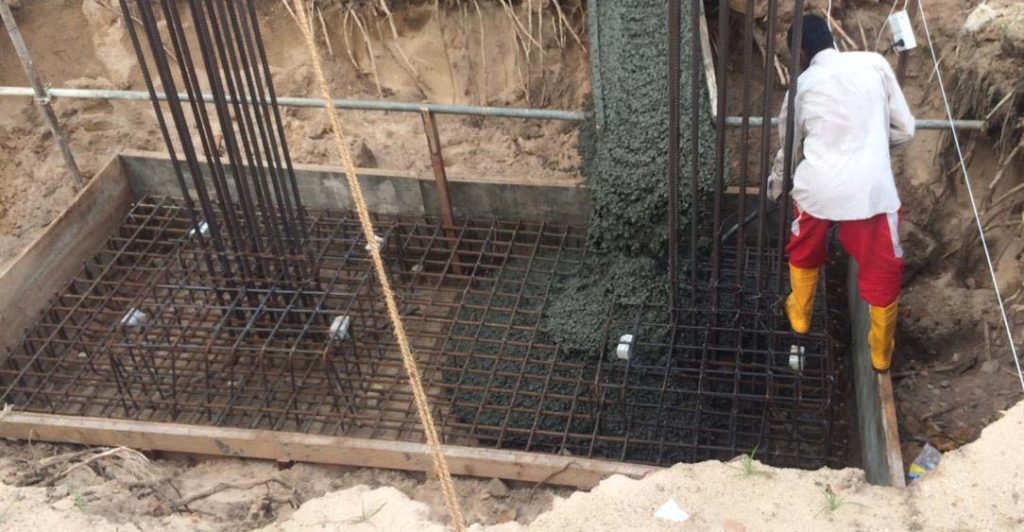
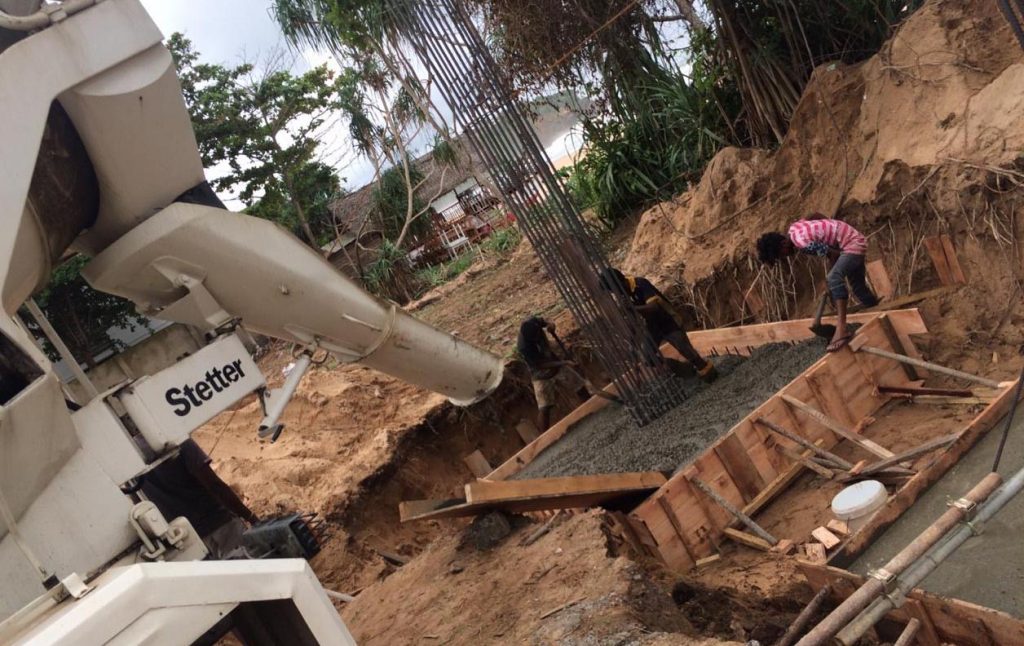
Underpinning is a process of strengthening the foundation of an existing structure that could be a building or any other type of structure.
This a good technique that is used in the construction and after the construction to improve the foundation. Generally, the improvement of the existing foundation and the ground condition is done to carry more load is done. This is one method that can be used for foundation improvements.
Underpinning is a technique that needs to be done with much care and careful supervision of the work. Incorrect approach, procedures, methods, etc could lead to failures of the structure.
This is mostly done for the existing structure. There could be a failure in the structure, severe damage to the structure, etc if not attended correctly.

Purpose of Underpinning – Why We do Underpinning
There are many reasons that we can discuss under this subject. Some of the most important reasons are listed below.
- Original Foundation is not strong or it is not stable
When the original foundation is not strong enough to carry the load applied from the superstructure, it shall be improved to avoid failures. Further, when there are different settlements due to the inadequacy of the foundations, improvement under the foundation could be done to enhance the bearing capacity of the soil.
- When the Usage of Structure is changing
There are possibilities of changing the usage of the buildings. When the applied loads are increasing due to these changes, underpinning is done as foundation improvement.
- Change Soil Properties Under the Foundation
When there are compressible soils, decomposing soils, etc, their properties are changing with time. As a result, foundations could settle. In these conditions, improvements in soil conditions are done.
- Consideration of Wrong Soil Characteristics
Consideration of wrong characteristics of soil or wrong classification of soils leads to incorrect estimation of soil design parameters such as being capacity, skin friction (positive skin friction and negative skin friction), etc.
This could lead to excessive settlement of the building even during the construction.
- Excavation for Adjoining Structure
There is a significant impact from the excavation on the existing structure. Proper shoring could avoid/minimize the influence. However, the most appropriate underpinning method shall be adopted.
- Increase the Load Carrying Capacity of Foundation
When it is required to increase the loads applied on the foundation, suitable underpinning methods are used.
For example, if we need to add a new floor to the existing structure rather than constructing it separately, improvement of the foundation will be done using the methods discussed in this article
- Improving is Economical than Building New Structure
As discussed previously too, building a new structure will cost more and more in terms of money or other resources.
For example, if we are building a new structure, we need to use the ground space available. However, this won’t be an issue if we add a floor to the existing structure.
Now, let’s discuss the available underpinning methods to achieve the above challenges.
Mainly there are two methods.
- Temporary Underpinning Methods
- Permanent Underpinning Methods
The temporary method includes ground freezing where which is done in tunneling when excavations are done below the groundwater table and groundwater control which is done to control the movement of the groundwater when there is a greater difficulty for the construction.
Let’s now move into the most essential part of this article.
The following figure indicates the available methods that are used widely.
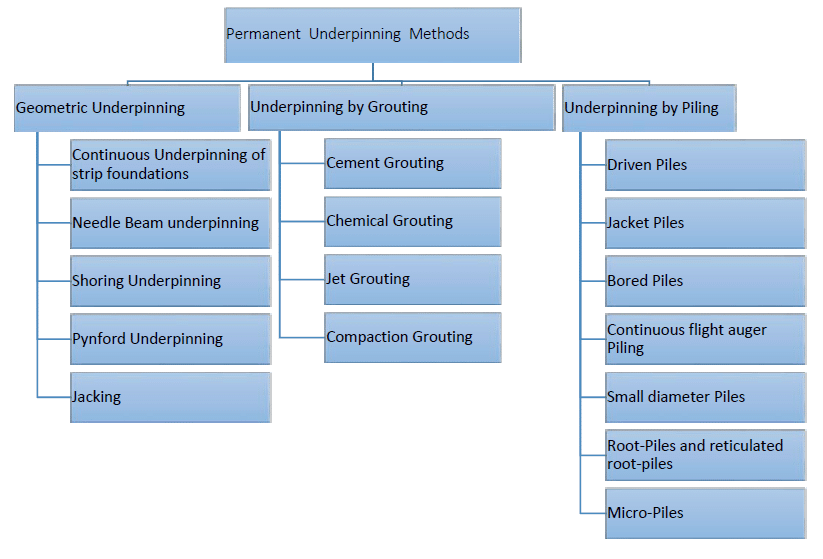
As indicated in the above chart, there are three main types of underpinning methods.
- Geometric underpinning
- Underpinning by grouting
- Underpinning by Piling
Let’s discussed some of the important methods in detail.
Underpinning by Grouting
Grouting methods are widely used as foundation improvements and they are more popular for improving the gradual soils.
It is easier to grout to penetrate when there are voids in the soil.
Cement Grouting
Cement grouting is effective in filling voids in granular soils where there are voids to move the cement grout. This is a useful technique in foundation improvements.
However, there are many other methods now developed that this process can be done much effectively. Therefore, cement grouting is not used widely compare to other methods.
The following advantages and enhancement can be observed in cement grouting.
- It reduces the permeability of the soil as voids are filled with cement grout
- It underpins the foundations
- It stabilizes the soil under the foundation and its strength is improved.
- This method can be used as excavation supports
Chemical Grouting
Chemical grouting transforms the granular soils into a very hard form that has very high strength.
This type of grouting is widely used for improving granular soil. When they inject into the soil, they bind the particles together and improve the soil bearing capacity.
Chemicals such as acrylamides, polyurethanes, acrylates, epoxies, and sodium silicates are widely used for chemical grouting.
Further, these methods are also same as the cement grouting and similar kind of advantages can be observed.
Jet Grouting
Jet grouting is also referred to as in-situ soil-cement columns.
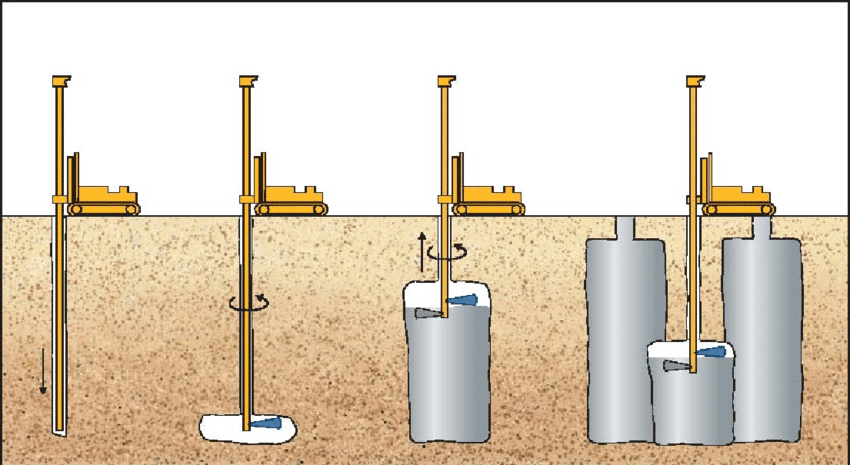
Let’s discuss the steps followed in jet grouting as indicated in the above figure.
- A hole will be drilled to a depth that the soil needs to be improved(stabilized and strengthened).
- Drilling could be done with the rotary device or using a water jet
- Then cut the soil by high-pressure jet (20-70 MPa) by rotating nozzle having diameter 2-3mm.
- Grout liquid is mixed with soil during this process.
- Then gradually, the soil-cement column is created. When it hardened, it solidifies the soil.
Mainly there are three get grouting techniques.
- Single Rod
- Dubble Rod
- Triple Rod
The following figure indicates the jet grouting done for a project.
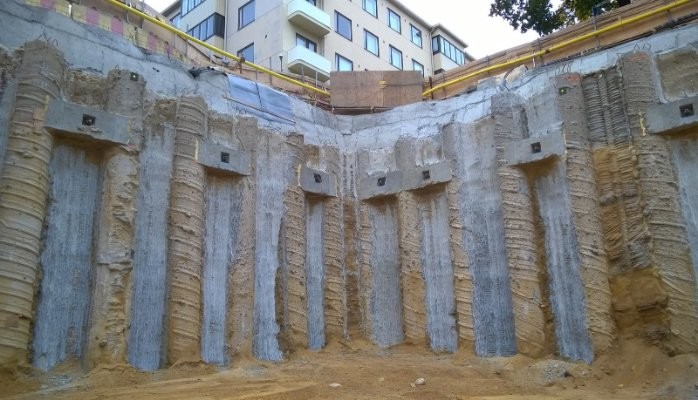

As we can see in the above figure, it gets grouting can be used very effectively in construction in addition it is using as an underpinning method.
Some of the advantages of jet grouting as follows.
- It reduces the settlement of the structure
- This can be done up to a depth of 80m
- This method can be used as excavation supports
- Reasonable cost saving
- Can be used even in tight spaces
- High safety
Compaction Grouting
This is a ground improvement method used to increase the density and the stiffness of the soil. This can be done for loose dense, granular soils.
Generally, a low slump mortar is injected into the soil layer with high pressure. The injection pressure is in the range of 1-4MPa.
The pressure injection pushes the surrounding soil and fills it with the injected mortar. The depth of the improvement can be carried out more than 10m depending on the available equipment.
The rate of the injection could be around 4-6m3 per hour. However, this could vary depending on the condition of the soil.
The following uses and advantages can be highlighted.
- Suitable for loose soils, collapsible soils, liquifiable soils, etc.
- Compaction grouting reduces the settlement of foundations
- Strenght of the soil increase and as a result soil bearing capacity increases.
- Increase the density of soil
Geometric Underpinning
When it is required to widen the foundations, increase the bearing capacity of soil under the foundation, increase the stiffness/density of soils under the foundations, these methods were used.
There are five main methods that were are discussing in this article as indicated in the chart shown at the beginning.
- The continuous underpinning of strip footings
- Needle beam underpinning
- Shoring underpinning
- Pynford underpinning
- Jacking
Let’s discuss each of these methods in detail.
Continuous Underpinning of Strip Footings – Pit Method
This method is also referred to as pier underpinning, pit underpinning, and pit pier.
Sometimes it is called as mass concrete underpinning method too.
These are very old methods used to improve the foundations when they subjected to failure or start to settle. This method is widely used to improve the foundation under the brick walls.
Here the failure does not mean collapse but it is starting the cracks in the building or in the referred structure due to the settlements.
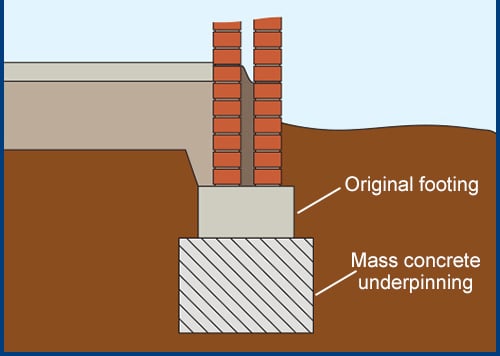
The following procedure is followed in this method.
- Firstly, pits are excavated under the foundation at regular intervals.
- The spacing of the pits could be 1-2m depending on the condition of the brick wall. If the quality of the brick is very poor, this spacing could not exceed 1.0m.
- Further, the spacing of the pits is determined from the arching action of the brick wall over the pit.
- Pit walls could be supported with timber as required.
- Depth of excavation could be done according to the soil conditions. Excavations are usually terminated at a soil layer that having the required bearing capacity.
- Then the pit will be filled with mass concrete.
- If other materials such as brickwork, masonry or precast concrete blocks, etc are used they shall be used with cement mortar.
- The final gap between the fill and the foundation (50-100mm) could be filled with a strong mix like 1:3 cement: sand.
Needle Beam Underpinning
Especially when the loads are not uniformly distributed this method is used to improve the foundations.
There are two main methods that we can use the needle beam method.
- Simply supported beam
- Cantilever beam
In these other methods, we cut a hole in the wall to support it by the beam send across the wall.
The type of beam could be reinforced concrete, timber, or steel. The use of steel beams is more preferred as it is easy to construct/fix when compared with the reinforced concrete beam.
- Cantilever Needle Beam
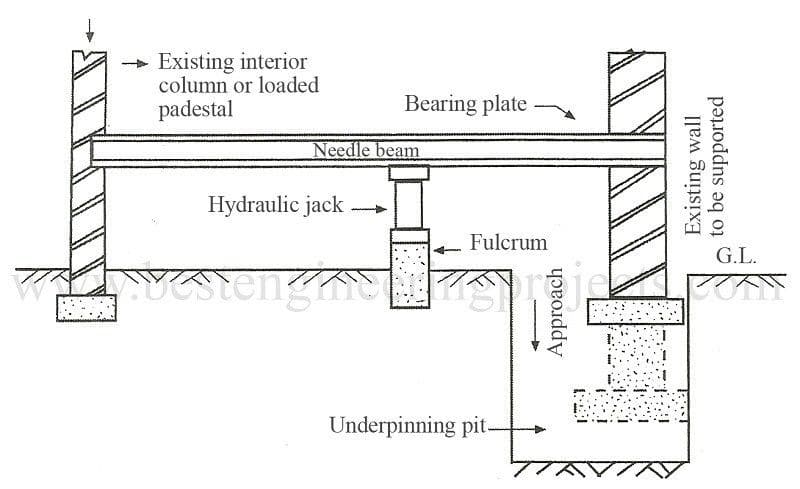
- Pile Supported Needle Beam
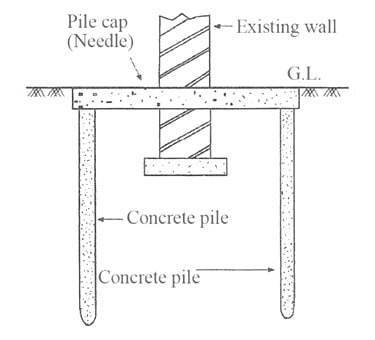
- Shallow Depth Supported Needle Beam
Supports of the needle beam could be precast piles, driven piles, or any other support rested on the soil as indicated in the above figures. The selection of the type of supports depends on the magnitude of the loads to be born by each support.
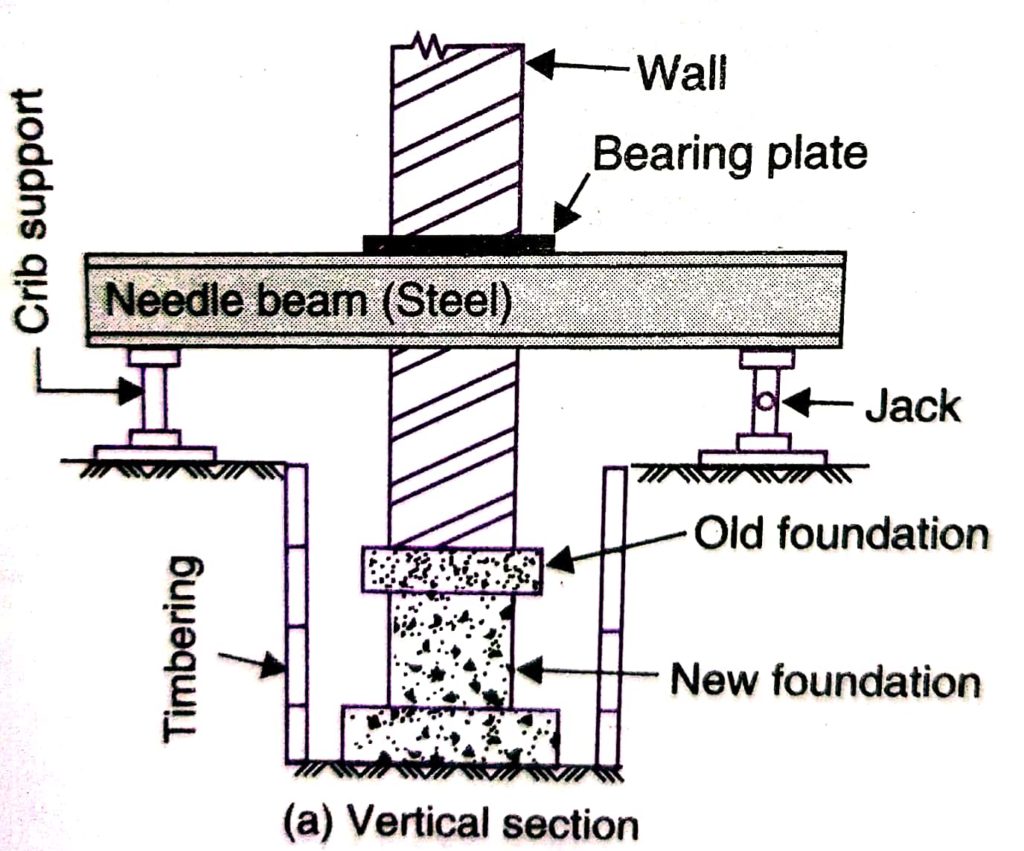
Shoring Underpinning
Stress or the load on the foundation needs to be released to carry out the underpinning of the foundation. Thus, walls are supported by different means to reduce the axial force on the foundation.
The following figure indicates such a method that can be used in foundation improvements.
Pynfored Underpinning
This is one of the very old methods used for improving the foundations.
Mainly used to support the brick walls.
Supports placed at closed spacing are sued to carry the load applied by walls. The base of the support is improved with strong mortar mixed to avoid the settlements.
The following figure indicates a wall supported in a similar manner.
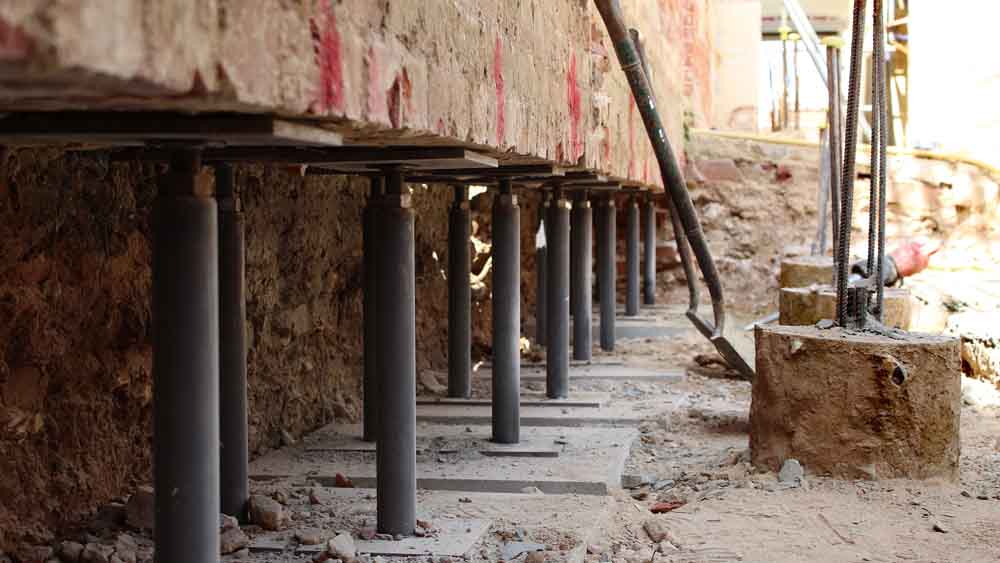

Jacking Methods
This method is commonly used in reinforced concrete structures. Not only for the foundation improvements but also for rectifying the columns, jacking is done.
Columns are supported by jacks placed on the had layer or concrete pad placed for this purpose. A force will be applied on the column in an upward direction equal to its axial force.
This could be done by jacking the beams around the column. When there are high axial loads, jacking at the ground floor will not be adequate as the beam could fail in shear. In such situations, the number of floors that need to be supported shall be checked by calculation.
Underpinning by Piling
As indicated in the chart above there are many methods that can be used for underpinning work.
Let’s list all of those methods.
- Driven Piles
- Jacked Piles
- Bored Piles
- Continuous Flight Auger Piling
- Small Diammeter Piles
- Root-Piles and Reticulated Root Piles
- Micro Piles
Let’s discuss each method in brief.
Driven Piles
Driven piles are more useful in underpinning work as it is easy to install and less time consuming for the installations.
However, there are considerable disadvantages that need to take into account.
- Installation can be done only on the outside of the building or structure.
- Excessive vibration during the installation and issues such as settlements, cracking, etc in existing structures.
- The old structure could damage the vibrations.
- A reasonable space is required for the installation.
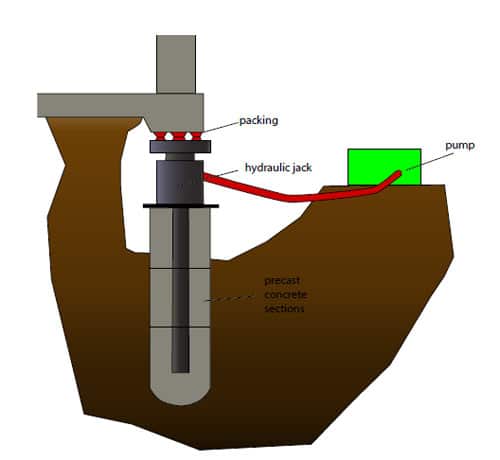
Jacked Piles
Jacked piles are a good alternative to the driven piles as they solve some of the issues.
Mainly it avoids the vibration of the ground cause during the installation.
Jacked piles are segmental concrete or steel piles.
Carrying out the improvement of the foundation is very difficult when the column loads are increasing.
Bored Piles
Construction-induced vibration and noise are comparatively lesser in bored pile foundations. Therefore, it can be used in sensitive areas.
However, it also needs clear space and higher headroom for installation.
Therefore, bored piles are also constructed outside the structure when the underpinnings of foundations are done. However, there are methods by which the installation can be done with low headroom. Tripod rigs can be used to install the board piles.
The following list of articles could be referred to for more information on foundations.
- How to Determine Foundation Type
- Types of Foundations [ a detailed study]
- Eccentrically Loaded Foundations
- Shallow Foundation Failure
- Pile Raft Foundations
- Mat Foundation Types, Design and Construction
- Pile foundations – Design, Construction and Testing Guide
- Pile Foundation Construction Problems and Solutions
- Driven Pile Foundations Design and Construction
- Settlement of Shallow Foundations


