It is crucial to have a thorough understanding of rust, a common form of corrosion, and the risk factors that can cause it in metallic materials. In this article, we will explore the chemical and environmental factors that can significantly increase the risk of rust, as well as preventive strategies and solutions for protecting steel and other metallic materials from corrosion.
There are a number of chemical and environmental factors that can cause corrosion, but one of the most common is rust. Rust is a type of corrosion that occurs when iron or steel is exposed to oxygen and moisture. This combination of elements creates a chemical reaction that causes the iron or steel to break down and form a reddish-brown oxide called rust.
One of the most significant risk factors for rust is exposure to water. Water can cause rust by itself, but it is often combined with other elements, such as salt, that can speed up the corrosion process. Other risk factors for rust include exposure to air pollution, chemicals, and acids.
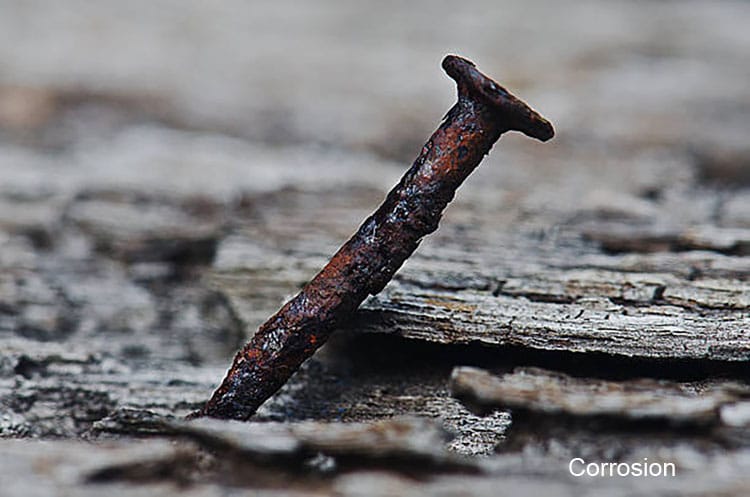
There are a number of ways to prevent rust from forming on steel and other metallic materials.
- One way is to coat the metal with a rust-resistant paint or sealant.
- Another way is to use galvanized steel, which is steel that has been treated with a zinc coating that prevents rust.
The article How to Prevent Corrosion discuss the more aspects in detail on preventive measures of the corrosion.
If rust has already formed on steel or other metallic materials, it is important to remove it as soon as possible. Rust can be removed with a variety of chemicals, but it is important to choose the right one for the type of metal that is affected.
While rust is a common and potentially damaging form of corrosion, it can be prevented with the right precautions. By understanding the risk factors and using the right solutions, it is possible to protect steel and other metallic materials from rust and keep them looking like new.


