Base isolation is a specialized type of structural engineering that is designed to protect structures from earthquakes, high winds, and other natural disasters. This article aims to provide an overview of the fundamentals of base isolation and its applications for civil engineers. Through this article, readers will gain a better understanding of base isolation and its role in safe and efficient building construction.
What is Base Isolation
One of the most important aspects of base isolation is the shock-absorbing mechanisms that are used to protect the structure from the forces of an earthquake. These mechanisms can be either active or passive. Active systems use sensors to detect the incoming seismic waves and then activate dampers that help to dissipate the energy of the waves. Passive systems, on the other hand, do not require any power source and instead rely on the materials used in the construction of the isolation system to absorb the energy of the seismic waves.
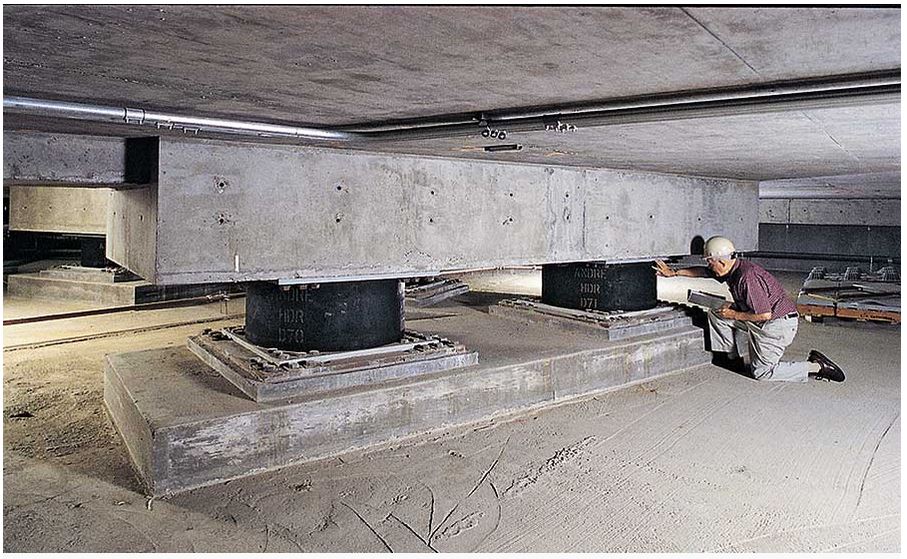
Another important aspect of base isolation is the use of special bearings that are designed to allow the structure to move independently from the ground. These bearings help to minimize the transfer of seismic waves from the ground to the structure and prevent the structure from collapsing during an earthquake.
Now that you have a better understanding of base isolation, you may be wondering how this technology is being used in the real world. Here are a few examples of base isolation in action:
- The Christchurch Cathedral in New Zealand was one of the first buildings to be retrofitted with base isolation technology. After the 2011 Christchurch earthquake, the Cathedral was badly damaged but did not collapse. This was thanks to the base isolation system that was installed prior to the earthquake.
- The palace of Westminster in London is another building that has been retrofitted with base isolation. The building is centuries old and is considered to be one of the most important buildings in the world. The base isolation system installed in the palace has been designed to protect the building from the effects of an earthquake.

These are just a few examples of how base isolation is being used to protect important structures from the devastating effects of earthquakes. As you can see, base isolation is a vital technology for civil engineers and should be considered for any new construction project.
Difference between Base Isolators and Seismic Dampers
Base isolators and seismic dampers are both used for earthquake protection. But, they work in different ways. Base isolators transfer forces between the building and its foundation. Seismic dampers absorb energy during an earthquake to reduce the effects of shaking that can cause damage to a building.
The primary difference between base isolators and seismic dampers is how they protect the structure when an earthquake occurs. Seismic dampers are typically installed near the top of a building, while base isolators are placed at the bottom or near the bottom of a building’s foundation system (usually connected to piles). How each type works depends on where you install one in your construction project.
Base isolators act as shock absorbers, dampening vibrations and controlled movements. Seismic dampers are a type of base isolator that is designed to isolate the building from seismic energy. They reduce the amount of movement felt in a building during an earthquake. Base isolators, or ‘shock mounts’ as they are sometimes called, are different from seismic dampers in several key ways: Seismic dampers incorporate springs, which add resistance to movement.
Base Isolators don’t have springs – they only rely on friction between two objects to slow down vibrations. Seismic dampers absorb energy through friction and heat produced by deformation (stretching) of the device itself. There is little deformation in base isolators. Because base isolators don’t rely on springs, there is less risk of failure due to fatigue through repeated use (i.e., wear and tear).
Type of Base Isolation Systems
The use of base isolation systems in buildings started in the 1960s, when they were introduced to reduce vulnerability to earthquake damage. Base isolation can be accomplished by the installation of mechanical springs and sliding devices, elastomeric bearings, or fluid-filled cylinders. In some cases, more than one technique is used. In a seismic event, base isolation systems are designed to allow relative motion between the ground and nonstructural building elements such as walls, partitions and floor slabs.

There are three main types of base isolation system:
Stationary base isolation systems
A stationary base isolation system uses a static, non-moving device to isolate the equipment from vibrations and other forces that occur during operation. These systems are used in heavy machinery and industrial plants where they provide vibration control.
Dynamic base isolation systems
A dynamic base isolation system is a hybrid between a stationary and a sliding type of system. They use springs and dampers to absorb energy by converting mechanical energy into thermal energy, thus preventing damage caused by the transmission of vibrations to the structure’s foundation. The main advantage of using dynamic base isolation systems is that they can be installed in any location without the need for major structural changes to the buildings’ foundations or modifications to its existing services.
Sliding base isolation systems
A sliding system uses four types of components: an elastomeric device, an elastomeric isolator, a spring/damper device and a guide rail. Each component works together to dissipate vibrations that may occur during operation. These systems can be used on both large and small structures such as buildings (including apartment buildings), factories, bridges, power plants and more.
In addition, classification can also be done as follows.
- Roller and ball bearings
- Sliding bearing
- Springs
- Elastomeric rubber bearings
What are Some of the Benefits of Base Isolation
One of the main benefits of base isolation is that it can protect structures from collapsing during an earthquake. This is thanks to the special bearings that are used in base isolation systems. These bearings help to minimize the transfer of seismic waves from the ground to the structure and prevent the structure from collapsing during an earthquake.
Another benefit of base isolation is that it can protect structures from high winds. This is because base isolation systems help to dissipate the energy of the wind. This can be especially important in typhoon-prone areas, where high winds can cause extensive damage to buildings.
Base isolation is a versatile technology that can be used to protect structures from a variety of natural disasters. If you are a civil engineer, it is important to be familiar with base isolation and to consider it for your next construction project.