The structural engineer and the construction team shall be aware of why does concrete crack on different occasions. There are many reasons for concrete cracking.
The cracking of concrete is very important to avoid as much as possible as it affects the durability of the structure and the structural stability if the structural element is cracked extensively.
Let’s see what the main reasons are for the cracking of concrete.
Why Does Concrete Crack
There could be many reasons for the cracking of concrete and there are different types of concrete cracks. Let’s see what are too common types of concrete cracks.
Cracking of Immure Concrete due to the Following Reasons
- Plastic Cracking
- Plastic Shrinkage Cracks
- Plastic Settlement Cracks
- Construction Movement
- Movement of Formwork
- Movement of subgrade
Reasons for Cracking of Hardened Concrete
- Physical Reasons for Cracking
- Shrinkable aggregates
- Drying shrinkage
- Crazing
- Chemical Reasons for Cracking of Concrete – Chemical attach on Concrete
- Corrosion of Reinforcements
- Alkali aggregate reaction
- Cement carbonation shrinkage
- Thermal Effects – Thermal Cracking of Concrete
- Freeze/thaws Cycles
- External seasonal temperature variations
- Early thermal Contractions
- Cracking of concrete caused by the rise of core temperature resulting to form delayed ettringites
- Structural Design Issues
- Accidental overload
- Cracking due to creep
- Cracking due to the consideration of incorrect design loads
- Cracking due to Wrong Construction Practices
Above are the key reasons for cracking concrete at each stage. In addition, let’s see a few related matters that we need to know.
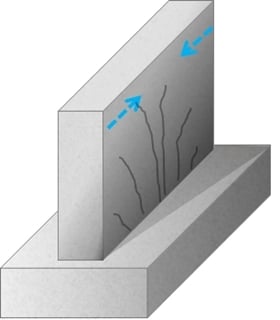
Why does New Concrete Crack / Why does Fresh Concrete Crack
New concrete does not have any stiffness other than the cohesion in the concrete mix. When the concrete getting harden, the stiffness is gradually generated.
When the concrete gets its volume reduces. It could result in the cracking of concrete. Those cracks could be identified as shrinkage cracks.
Further, after placing the concrete, if we do not do the curing of concrete at right time and write manager concrete could crack. The following can be can listed as the main reasons for cracking of new concrete.
- Excessing evaporation of moisture from the concrete surface
- High-temperature difference between the surface and core in large concrete
- Higher temperature gradient in thick concretes.
- In adequate reinforcement to bear the tensile stresses developed in the immature concrete.
Why does concrete crack while drying or Why does concrete crack when drying
Concrete shrinks when it gets stiffened or hardened. This shrinkage of the concrete lead to developing the tensile stresses in the concrete. These tensile stresses lead to the cracking of concrete.
If there are adequate reinforcements provided to bear the stress developed in the concrete, it could be able to avoid these types of concrete cracks.
Further, when the concrete gets dry, the water in the concrete evaporates. Evaporation reduces the volume of concrete and its load to develop tensile stresses. Crack forms in this manner are called drying shrinkage cracking.
Why do Concrete Slab Crack / Why do Concrete Floors Crack
The concrete slab is not a thick element generally. There won’t be a very high rise in the temperature of the concrete. Therefore, the cracking of concrete due to the thermal effect is less possible.
However, drying of concrete due to the external temperature rise is possible. Therefore, drying shrinkage cracking could occur.
Adequate curing of slab concrete could lead to these types of cracks.
Apart from that, if the slab thickness is greater than 200mm, there may be cracks in the concrete, due to the thermal effects too. Providing adequate reinforcement to avoid cracking could be done.
Why does Self Leveling Concrete Crack
In general, self-levelling concrete is also a kind of concrete that has almost similar properties to other concrete. The ability to be self-level is a special feature.
The workability of the self-level concrete is higher. It could be maintained by increasing the water content or adding a water-reducing admixture.
A higher rate of evaporation and drying shrinkage could be reasons for the cracking of self-levelling concrete.
With clarifications, you could know why concrete cracks.
Cracking of concrete may not be avoidable. However, we could not let the concrete crack in a manner that affect the durability of the structure and the structural stability.
Related Articles
- Early Thermal Cracking [calculate R/F requirements]
- Effect of Construction Practices on Cracking
- Cracking of Concrete [ basics, types and causes]
- Physical Reasons for Cracking
- Fundamental of Cracking of Immature Concrete
- Foundation Cracks types why they serious
- Cracks in Basement Wall [a detailed study]
- What is Spalling of Concrete – causes and repair
- 20 Factors Affecting Durability of Concrete
- Durability of Concrete [Requirements and Problems]
- Vibration of Concrete [methods and correct procedure]
- 6 Factors Affecting Curing Time of Concrete
- 11 Methods for Curing of Concrete
- A Detailed Study on Concrete[from scratch]
- Types of Shrinkage in Concrete [detailed study]